Community health workers and mHealth systems for hearing screening in rural Nicaraguan schoolchildren
- PMID: 35938885
- PMCID: PMC9359107
- DOI: 10.7189/jogh.12.04060
Community health workers and mHealth systems for hearing screening in rural Nicaraguan schoolchildren
Abstract
Background: We aimed to investigate the effectiveness of using minimally trained community health workers (CHW) to screen schoolchildren in rural Nicaragua for hearing loss using a tablet-based audiometric system integrated with asynchronous telehealth evaluations and mobile health (mHealth) appointment reminders.
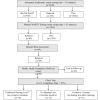
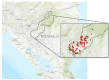
Methods: A population-based survey was conducted using community health workers (CHWs) to perform tablet-based audiometry, asynchronous telehealth evaluations, and mHealth reminders to screen 3398 school children (7-9 years of age) in 92 rural Nicaraguan communities. The accuracy of screening, test duration, testing efficiency, telehealth data validity, and compliance with recommended clinic visits were analyzed.
Results: Minimally trained CHWs successfully screened children within remote rural schools with automated audiometry (test duration = 5.8 minutes) followed by manual audiometry if needed (test duration = 4.3 minutes) with an estimated manual audiometry validity of 98.5% based on a review of convergence patterns. For children who were referred based on audiometry, the otoscopy and tympanometry obtained during telehealth evaluations were high quality (as reviewed by 3 experts) in 44.6% and 80.1% of ears, respectively. A combination of automated short message service (SMS) text messages and voice reminders resulted in a follow-up compliance of 75.2%. No families responded to SMS messages alone.
Conclusions: Tablet-based hearing screening administered by minimally trained CHWs is feasible and effective in low- and middle-income countries. Manual audiometry was as efficient as automated audiometry in this setting. The physical exam tasks of otoscopy and tympanometry require additional training. Mobile phone messages improve compliance for confirmatory audiometry, but the utility of SMS messaging alone is unclear in this population.
Copyright © 2022 by the Journal of Global Health. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of interest: The authors completed the ICMJE Disclosure of Interest Form (available upon request from the corresponding author) and disclose no relevant interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
School Hearing Screening With a Portable, Tablet-Based, Noise-Attenuating Audiometric Headset in Rural Nicaragua.Otol Neurotol. 2022 Dec 1;43(10):1196-1204. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000003692. Otol Neurotol. 2022. PMID: 36351228
-
Assessing the efficacy of asynchronous telehealth-based hearing screening and diagnostic services using automated audiometry in a rural South African school.S Afr J Commun Disord. 2018 Jul 5;65(1):e1-e9. doi: 10.4102/sajcd.v65i1.582. S Afr J Commun Disord. 2018. PMID: 30035608 Free PMC article.
-
Hearing Norton Sound: a community randomised trial protocol to address childhood hearing loss in rural Alaska.BMJ Open. 2019 Jan 15;9(1):e023078. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-023078. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 30782695 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying and Treating Childhood Hearing Loss in Rural Alaska -- The Hearing Norton Sound Study [Internet].Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2022 Feb. Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2022 Feb. PMID: 39504398 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Mobile health (mHealth) approaches and lessons for increased performance and retention of community health workers in low- and middle-income countries: a review.J Med Internet Res. 2013 Jan 25;15(1):e17. doi: 10.2196/jmir.2130. J Med Internet Res. 2013. PMID: 23353680 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Globally applicable solution to hearing loss screening: a diagnostic accuracy study of tablet-based audiometry.BMJ Open. 2025 May 22;15(5):e097550. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-097550. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40404318 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The PEN Fa'aSamoa Initiative: An Integrated Platform for Hearing and Vision Screening in Samoa.Glob Pediatr Health. 2023 Oct 9;10:2333794X231203504. doi: 10.1177/2333794X231203504. eCollection 2023. Glob Pediatr Health. 2023. PMID: 37822475 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Krug E, Cieza A, Chadha S, Sminkey L, Martinez R, Stevens G, et al. Childhood hearing loss: strategies for prevention and care. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016.
-
- World Report on Hearing. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
