Systemic inflammatory biomarkers as predictive and prognostic factors in men with metastatic castration-refractory prostate cancer treated with docetaxel therapy: a comprehensive analysis in a German real-world cohort
- PMID: 35939112
- PMCID: PMC10314827
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-022-04220-w
Systemic inflammatory biomarkers as predictive and prognostic factors in men with metastatic castration-refractory prostate cancer treated with docetaxel therapy: a comprehensive analysis in a German real-world cohort
Abstract
Purpose: Advances in therapy of metastatic castration-refractory prostate cancer (mCRPC) resulted in more therapeutic options and led to a higher need of predictive/prognostic biomarkers. Systemic inflammatory biomarkers could provide the basis for personalized treatment selection. This study aimed to assess the modified Glasgow Prognostic Score (mGPS), the neutrophile-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and the systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) in men with mCRPC under docetaxel.
Methods: Patients with mCRPC and taxane chemotherapy at a tertiary care centre between 2010 and 2019 were screened retrospectively. The biomarkers mGPS, NLR, PLR and SII were assessed and analyzed for biochemical/radiologic response and survival.
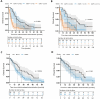
Results: We included 118 patients. Of these, 73 (61.9%) had received docetaxel as first-line, 31 (26.2%) as second-line and 14 (11.9%) as third-line treatment. For biochemical response, mGPS (odds ratio (OR) 0.54, p = 0.04) and PLR (OR 0.63, p = 0.04) were independent predictors in multivariable analysis. SII was significant in first-line cohort only (OR 0.29, p = 0.02). No inflammatory marker was predictive for radiologic response. In multivariable analysis, mGPS and NLR (hazard ratio (HR) 1.71 and 1.12, both p < 0.01) showed significant association with OS in total cohort and mGPS in the first-line cohort (HR 2.23, p < 0.01). Haemoglobin (Hb) and alkaline phosphatase (AP) showed several significant associations regarding 1 year, 3 year, OS and biochemical/radiologic response.
Conclusions: Pre-treatment mGPS seems a promising prognostic biomarker. A combination of mGPS, NLR and further routine markers (e.g., Hb and AP) could yield optimized stratification for treatment selection. Further prospective and multicentric assessment is needed.
Keywords: Biomarker; Metastatic castration-refractory prostate cancer; Pre-treatment; Prognosis; Systemic inflammatory markers.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Cancer Stat Facts: Prostate Cancer. Retrieved 06.11.2021, from https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/prost.html.
-
- Armstrong AJ, Garrett-Mayer E, de Wit R, Tannock I, Eisenberger M (2010) Prediction of survival following first-line chemotherapy in men with castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16(1):203–211 - PubMed
-
- Cornford P, van den Bergh RCN, Briers E, Van den Broeck T, Cumberbatch MG, De Santis M, Fanti S, Fossati N, Gandaglia G, Gillessen S, Grivas N, Grummet J, Henry AM, der Kwast THV, Lam TB, Lardas M, Liew M, Mason MD, Moris L, Oprea-Lager DE, der Poel HGV, Rouvière O, Schoots IG, Tilki D, Wiegel T, Willemse PM, Mottet N (2021) EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. part II-2020 update: treatment of relapsing and metastatic prostate cancer. Eur Urol 79(2):263–282 - PubMed
-
- Dolan RD, Laird BJA, Horgan PG, McMillan DC (2018) The prognostic value of the systemic inflammatory response in randomised clinical trials in cancer: a systematic review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 132:130–137 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources