Wnt3a/YTHDF1 Regulated Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain Via TNF-α/IL-18 Expression in the Spinal Cord
- PMID: 35939138
- PMCID: PMC11412420
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-022-01267-8
Wnt3a/YTHDF1 Regulated Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain Via TNF-α/IL-18 Expression in the Spinal Cord
Abstract
Oxaliplatin is widely used in cancer treatment, however, many patients will suffer from neuropathic pain (NP) induced by it at the same time. Therefore exploring the mechanism and founding novel target for this problem are needed. In this study, YTHDF1 showed upregulation in oxaliplatin treated mice. As m6A is known as conserved and it widely functions in numerous physiological and pathological processes. Therefore, we focused on exploring the molecular mechanism of whether and how YTHDF1 functions in NP induced by oxaliplatin. IHC and western blotting were conducted to measure proteins. Intrathecal injection for corresponding siRNAs in C57/BL6 mice or spinal microinjection for virus in YTHDF1flox/flox mice were applied to specially knockdown the expression of molecular. Von Frey, acetone test and ethyl chloride (EC) test were applied to evaluate NP behavior. YTHDF1, Wnt3a, TNF-α and IL-18 were increased in oxaliplatin treated mice, restricted the molecular mentioned above respectively can significantly attenuate oxaliplatin-induced NP, including the mechanical allodynia and cold allodynia. Silencing YTHDF1 and inhibiting Wnt3a and Wnt signaling pathways can reduce the enhancement of TNF-α and IL-18, and the decreasing of the upregulation of YTHDF1 can be found when inhibiting Wnt3a and Wnts signaling pathways in oxaliplatin treated mice. Our study indicated a novel pathway that can contribute to oxaliplatin-induced NP, the Wnt3a/YTHDF1 to cytokine pathway, which upregulating YTHDF1 functioned as the downstream of Wnt3a signal and promoted the translation of TNF-α and IL-18 in oxaliplatin treated mice.
Keywords: IL18; Neuropathic pain; TNF alpha; Wnt; YTHDF1.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
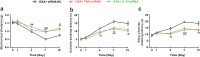
Similar articles
-
Anti-allodynic effect of Buja in a rat model of oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy via spinal astrocytes and pro-inflammatory cytokines suppression.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jan 14;17(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1556-z. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28088201 Free PMC article.
-
Zingiber officinale Roscoe Rhizomes Attenuate Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Mice.Molecules. 2021 Jan 21;26(3):548. doi: 10.3390/molecules26030548. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33494465 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-146a-5p attenuates neuropathic pain via suppressing TRAF6 signaling in the spinal cord.Brain Behav Immun. 2015 Oct;49:119-29. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.04.018. Epub 2015 May 5. Brain Behav Immun. 2015. PMID: 25957028
-
TRAF6 upregulation in spinal astrocytes maintains neuropathic pain by integrating TNF-α and IL-1β signaling.Pain. 2014 Dec;155(12):2618-2629. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2014.09.027. Epub 2014 Oct 19. Pain. 2014. PMID: 25267210 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic analysis of critical genes and pathways identified a signature of neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury.Eur J Neurosci. 2022 Jul;56(2):3991-4008. doi: 10.1111/ejn.15693. Epub 2022 May 27. Eur J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35560852 Review.
Cited by
-
The function and clinical implication of YTHDF1 in the human system development and cancer.Biomark Res. 2023 Jan 17;11(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40364-023-00452-1. Biomark Res. 2023. PMID: 36650570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Primary Cilium and its Hedgehog Signaling in Nociceptors Contribute to Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 26:rs.3.rs-3812442. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3812442/v1. Res Sq. 2024. PMID: 38464172 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
The Nociceptor Primary Cilium Contributes to Mechanical Nociceptive Threshold and Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain.J Neurosci. 2024 Nov 20;44(47):e1265242024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1265-24.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39349056 Free PMC article.
-
The YTHDF1-TRAF6 pathway regulates the neuroinflammatory response and contributes to morphine tolerance and hyperalgesia in the periaqueductal gray.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Dec 22;19(1):310. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02672-y. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 36550542 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrandrine alleviates oxaliplatin-induced mechanical allodynia via modulation of inflammation-related genes.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Feb 14;17:1333842. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1333842. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38419796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acevedo Rua L, Mumme M, Manferdini C, Darwiche S, Khalil A, Hilpert M, Buchner DA, Lisignoli G, Occhetta P, von Rechenberg B, Haug M, Schaefer DJ, Jakob M, Caplan A, Martin I, Barbero A, Pelttari K (2021) Engineered nasal cartilage for the repair of osteoarthritic knee cartilage defects. Sci Transl Med 13:eaaz1499 - PubMed
-
- Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53:55–63 - PubMed
-
- Ciani L, Salinas PC (2005) WNTs in the vertebrate nervous system: from patterning to neuronal connectivity. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:351–362 - PubMed
-
- Clevers H, Nusse R (2012) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 149:1192–1205 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

