Application of reverse vaccinology to design a multi-epitope subunit vaccine against a new strain of Aeromonas veronii
- PMID: 35939149
- PMCID: PMC9358925
- DOI: 10.1186/s43141-022-00391-8
Application of reverse vaccinology to design a multi-epitope subunit vaccine against a new strain of Aeromonas veronii
Abstract
Background: Aeromonas veronii is one of the most common pathogens of freshwater fishes that cause sepsis and ulcers. There are increasing numbers of cases showing that it is a significant zoonotic and aquatic agent. Epidemiological studies have shown that A. veronii virulence and drug tolerance have both increased over the last few years as a result of epidemiological investigations. Cadaverine reverse transporter (CadB) and maltoporin (LamB protein) contribute to the virulence of A. veronii TH0426. TH0426 strain is currently showing severe cases on fish species, and its resistance against therapeutic has been increasing. Despite these devastating complications, there is still no effective cure or vaccine for this strain of A.veronii.
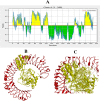
Results: In this regard, an immunoinformatic method was used to generate an epitope-based vaccine against this pathogen. The immunodominant epitopes were identified using the CadB and LamB protein of A. veronii. The final constructed vaccine sequence was developed to be immunogenic, non-allergenic as well as have better solubility. Molecular dynamic simulation revealed significant binding stability and structural compactness. Finally, using Escherichia coli K12 as a model, codon optimization yielded ideal GC content and a higher CAI value, which was then included in the cloning vector pET2+ (a).
Conclusion: Altogether, our outcomes imply that the proposed peptide vaccine might be a good option for A. veronii TH0426 prophylaxis.
Keywords: A. Veronii TH0426; E. coli K12; Epitopes; MD simulation; Vaccine.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


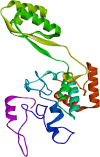


References
-
- Chandrarathna HPSU, et al. Outcome of co-infection with opportunistic and multidrug resistant Aeromonas hydrophila and A. veronii in zebrafish: identification, characterization, pathogenicity and immune responses. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018;80:573–581. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.06.049. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hassan MA, et al. Molecular identification and epizootiology of Aeromonas veronii infection among farmed Oreochromis niloticus in Eastern Province, KSA. Egyptian J Aquatic Res. 2017;43(2):161–167. doi: 10.1016/j.ejar.2017.06.001. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
