Atropopeptides are a Novel Family of Ribosomally Synthesized and Posttranslationally Modified Peptides with a Complex Molecular Shape
- PMID: 35939298
- PMCID: PMC9826248
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202208361
Atropopeptides are a Novel Family of Ribosomally Synthesized and Posttranslationally Modified Peptides with a Complex Molecular Shape
Abstract
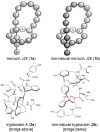
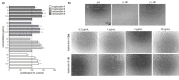
Biomacromolecules are known to feature complex three-dimensional shapes that are essential for their function. Among natural products, ambiguous molecular shapes are a rare phenomenon. The hexapeptide tryptorubin A can adopt one of two unusual atropisomeric configurations. Initially hypothesized to be a non-ribosomal peptide, we show that tryptorubin A is the first characterized member of a new family of ribosomally synthesized and posttranslationally modified peptides (RiPPs) that we named atropopeptides. The sole modifying enzyme encoded in the gene cluster, a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase, is responsible for the atropospecific formation of one carbon-carbon and two carbon-nitrogen bonds. The characterization of two additional atropopeptide biosynthetic pathways revealed a two-step maturation process. Atropopeptides promote pro-angiogenic cell functions as indicated by an increase in endothelial cell proliferation and undirected migration. Our study expands the biochemical space of RiPP-modifying enzymes and paves the way towards the chemoenzymatic utilization of atropopeptide-modifying P450s.
Keywords: Atropisomerism; Cytochrome P450 Monooxygenase; Genome Mining; RiPPs; Stereoisomerism.
© 2022 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploration, expansion and definition of the atropopeptide family of ribosomally synthesized and posttranslationally modified peptides.Chem Sci. 2024 Sep 10;15(42):17506-23. doi: 10.1039/d4sc03469d. Online ahead of print. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 39371454 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogeny-guided discovery of a promiscuous P450 macrocyclase for the production of diverse atropopeptides.Chem Sci. 2025 Aug 6;16(35):16240-16249. doi: 10.1039/d5sc03525b. eCollection 2025 Sep 10. Chem Sci. 2025. PMID: 40822110 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Cytochrome P450 Catalyzed Post-translational Macrocyclization of Ribosomal Peptides.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2023 Nov 13;62(46):e202311533. doi: 10.1002/anie.202311533. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2023. PMID: 37767859
-
Cytochromes P450 involved in bacterial RiPP biosyntheses.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Feb 17;50(1):kuad005. doi: 10.1093/jimb/kuad005. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36931895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of novel fungal RiPP biosynthetic pathways and their application for the development of peptide therapeutics.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Jul;103(14):5567-5581. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09893-x. Epub 2019 May 31. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31147756 Review.
Cited by
-
A stereodivergent multicomponent approach for the synthesis of C-N atropisomeric peptide analogues.Chem Sci. 2024 Sep 16;15(40):16743-51. doi: 10.1039/d4sc04700a. Online ahead of print. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 39323517 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics-guided discovery of biaryl-linked lasso peptides.Chem Sci. 2023 Oct 30;14(45):13176-13183. doi: 10.1039/d3sc02380j. eCollection 2023 Nov 22. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 38023510 Free PMC article.
-
Proteases Involved in Leader Peptide Removal during RiPP Biosynthesis.ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2023 Dec 13;4(1):20-36. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomedchemau.3c00059. eCollection 2024 Feb 21. ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2023. PMID: 38404746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide Crosslinking by a Class of Plant Copper Enzymes.Trends Chem. 2024 Nov;6(11):649-655. doi: 10.1016/j.trechm.2024.09.002. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Trends Chem. 2024. PMID: 39877592
-
Aromatic side-chain crosslinking in RiPP biosynthesis.Nat Chem Biol. 2025 Feb;21(2):168-181. doi: 10.1038/s41589-024-01795-y. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Nat Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 39814993 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- None
-
- Creighton T. E., Proteins: structures and molecular properties , 2nd ed., W. H. Freeman, New York, 1993.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

