Acute coronary syndrome versus acute myocarditis in young adults-value of speckle tracking echocardiography
- PMID: 35939417
- PMCID: PMC9359587
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271483
Acute coronary syndrome versus acute myocarditis in young adults-value of speckle tracking echocardiography
Abstract
Purpose: Comparing myocarditis with an acute coronary syndrome (ACS)-like presentation and acute myocardial infarction (AMI) poses an important clinical challenge. The purpose of the study was to investigate the diagnostic value of the clinical, laboratory and especially echocardiographic characteristics including speckle tracking echocardiography (STE) of patients with ACS-like myocarditis and AMI.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis comparing 69 symptomatic patients (≤ 45 years old), hospitalized at the Department of Interventional Cardiology (Medical University of Lodz, Poland) between April 2014 and June 2021 with an initial diagnosis of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.
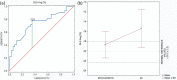
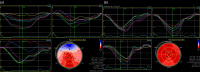
Results: 37 patients with the cardiac magnetic resonance-confirmed acute myocarditis and 32 patients diagnosed with AMI based on the clinical presentation, electrocardiogram and the presence of a culprit lesion on the coronary angiography were analysed including echocardiography parameters. On STE analysis an average global longitudinal (GLS), radial and circumferential strain including three-layers observation were significantly lower (absolute value) in patients with AMI versus acute myocarditis (p<0.05). There was no significant difference in Endo/Epi ratio (p = 0.144) between the groups. An average GLS < (-17.5) represented the optimal cut-off value for the myocarditis diagnosis.
Conclusion: In patients with AMI a significant reduction of global and three-layers strains compared to patients with myocarditis was detected. Furthermore, our analysis also confirmed the discriminative pattern of myocardial injury between the groups.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Usefulness of layer-specific strain for identifying complex CAD and predicting the severity of coronary lesions in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome: Compared with Syntax score.Int J Cardiol. 2016 Nov 15;223:1045-1052. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.08.277. Epub 2016 Aug 18. Int J Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27592047
-
A Comparison Between Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Regional and Global Longitudinal Strain Echocardiography to Evaluate Complex Coronary Lesions in Patients With Non-ST-Segment Elevation Acute Coronary Syndrome.Cureus. 2022 Apr 11;14(4):e24025. doi: 10.7759/cureus.24025. eCollection 2022 Apr. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35444922 Free PMC article.
-
Usefulness of a multiparametric evaluation including global longitudinal strain for an early diagnosis of acute myocarditis.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021 Nov;37(11):3203-3211. doi: 10.1007/s10554-021-02299-9. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34086168 Free PMC article.
-
Role of two-dimensional strain echocardiographic parameters in suspected acute coronary syndrome patients with initial non-diagnostic electrocardiogram and troponins: An observational study.Echocardiography. 2023 Aug;40(8):802-809. doi: 10.1111/echo.15647. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Echocardiography. 2023. PMID: 37417914
-
Late Detection of Left Ventricular Dysfunction Using Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography in Patients with History of Nonsevere Acute Myocarditis.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2017 Aug;30(8):756-762. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2017.04.002. Epub 2017 Jun 7. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2017. PMID: 28599827
Cited by
-
Quantification of hs-Troponin Levels and Global Longitudinal Strain among Critical COVID-19 Patients with Myocardial Involvement.J Clin Med. 2024 Jan 8;13(2):352. doi: 10.3390/jcm13020352. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38256486 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Lyme Carditis-A Case Series and Review of Literature.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024 Dec 25;12(1):2. doi: 10.3390/jcdd12010002. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024. PMID: 39852280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune myocarditis induced by sintilimab therapy: A case report.Exp Ther Med. 2024 Jun 25;28(2):333. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12622. eCollection 2024 Aug. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 39006500 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

