Negative emotional reactions to criticism: Perceived criticism and source affects extent of hurt and relational distancing
- PMID: 35939429
- PMCID: PMC9359543
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271869
Negative emotional reactions to criticism: Perceived criticism and source affects extent of hurt and relational distancing
Abstract
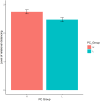
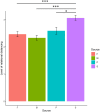
Criticism is commonly perceived as hurtful and individuals may respond differently to criticism originating from different sources. However, the influence of an individual's perception of criticism in their social relationships on negative emotional reactions to criticism has not been examined across different relational contexts. The present study investigated the influence of perceived criticism and relational contexts-mother, father, romantic partner, and workplace supervisor-on the feelings of hurt and relational distancing experienced upon receiving criticism. Participants (N = 178) completed the Perceived Criticism Measure and read vignettes describing scenarios of personally directed criticism in the four relational contexts. Significant main effects of perceived criticism and source were found on levels of relational distancing. Participants who perceived their relational partner to be more critical experienced greater distancing upon receiving criticism from them. Greater relational distancing was experienced for criticism received from workplace supervisors compared to mothers, fathers and romantic partners. Results indicate that emotional reactions and relationship outcomes in response to criticism can differ based on individual differences and relational context, suggesting their role in relationship maintenance and development of psychopathology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Perceptions of sexism interact with perceived criticism on women's response to sexist remarks in different relationship types.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 26;13(1):18393. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44952-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37884572 Free PMC article.
-
Disapproval from romantic partners, friends and parents: Source of criticism regulates prefrontal cortex activity.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 2;15(10):e0229316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229316. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33006966 Free PMC article.
-
Social Anxiety Disorder and Perceived Criticism in Intimate Relationships: Comparisons With Normal and Clinical Control Groups.Behav Ther. 2019 Jan;50(1):241-253. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2018.05.005. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Behav Ther. 2019. PMID: 30661563
-
Communal relational context (or lack thereof) shapes emotional lives.Curr Opin Psychol. 2017 Oct;17:176-183. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2017.07.023. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Curr Opin Psychol. 2017. PMID: 28950966 Review.
-
Emotional responses to interpersonal rejection.Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2015 Dec;17(4):435-41. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2015.17.4/mleary. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26869844 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sources of attitudes towards parent-child co-sleeping and their effects: A systematic scoping review.Fam Process. 2024 Dec;63(4):2484-2504. doi: 10.1111/famp.13022. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Fam Process. 2024. PMID: 38837802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deutsch M. The interpretation of praise and criticism as a function of their social context. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology. 1961; 62(2), 391–400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical