Ovariectomy reduces cholinergic modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission in the rat entorhinal cortex
- PMID: 35939438
- PMCID: PMC9359571
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271131
Ovariectomy reduces cholinergic modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission in the rat entorhinal cortex
Abstract
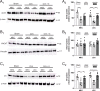
Estrogens are thought to contribute to cognitive function in part by promoting the function of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons that project to the hippocampus and cortical regions including the entorhinal cortex. Reductions in estrogens may alter cognition by reducing the function of cholinergic inputs to both the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex. In the present study, we assessed the effects of ovariectomy on proteins associated with cholinergic synapses in the entorhinal cortex. Ovariectomy was conducted at PD63, and tissue was obtained on PD84 to 89 to quantify changes in the degradative enzyme acetylcholinesterase, the vesicular acetylcholine transporter, and muscarinic M1 receptor protein. Although the vesicular acetylcholine transporter was unaffected, ovariectomy reduced both acetylcholinesterase and M1 receptor protein, and these reductions were prevented by chronic replacement of 17β-estradiol following ovariectomy. We also assessed the effects of ovariectomy on the cholinergic modulation of excitatory transmission, by comparing the effects of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor eserine on evoked excitatory synaptic field potentials in brain slices obtained from intact rats, and from ovariectomized rats with or without 17β-estradiol replacement. Eserine is known to prolong the effects of endogenously released acetylcholine, resulting in an M1-like mediated reduction of glutamate release at excitatory synapses. The reduction in excitatory synaptic potentials in layer II of the entorhinal cortex induced by 15-min application of 10 μM eserine was greatly reduced in slices from ovariectomized rats as compared to intact rats and ovariectomized rats with replacement of 17β-estradiol. The reduced modulatory effect of eserine is consistent with the observed changes in cholinergic proteins, and suggests that reductions in 17β-estradiol following ovariectomy lead to impaired cholinergic function within the entorhinal cortex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
17β-Estradiol reduces inhibitory synaptic currents in entorhinal cortex neurons through G protein-coupled estrogen receptor-1 activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase.Hippocampus. 2024 Sep;34(9):454-463. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23621. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Hippocampus. 2024. PMID: 39150316
-
Cholinergic receptor activation induces a relative facilitation of synaptic responses in the entorhinal cortex during theta- and gamma-frequency stimulation of parasubicular inputs.Neuroscience. 2013 Jan 29;230:72-85. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.11.026. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23201257
-
Contribution of muscarinic M1 receptors to the cholinergic suppression of synaptic responses in layer II of the entorhinal cortex.Neurosci Lett. 2013 Oct 25;554:11-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.08.050. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Neurosci Lett. 2013. PMID: 24012918
-
Cholinergic suppression of excitatory synaptic responses in layer II of the medial entorhinal cortex.Hippocampus. 2007;17(2):103-13. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20249. Hippocampus. 2007. PMID: 17146776
-
Immunolesion by 192IgG-saporin of rat basal forebrain cholinergic system: a useful tool to produce cortical cholinergic dysfunction.Prog Brain Res. 1996;109:253-64. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62109-3. Prog Brain Res. 1996. PMID: 9009714 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of biological sex with clinical outcomes and biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease in adults with Down syndrome.Brain Commun. 2023 Mar 17;5(2):fcad074. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcad074. eCollection 2023. Brain Commun. 2023. PMID: 37056479 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Regular Exercise and Intermittent Fasting on Neurotransmitters, Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Cortex of Ovariectomized Rats.Nutrients. 2023 Oct 6;15(19):4270. doi: 10.3390/nu15194270. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37836554 Free PMC article.
-
A Developmental Switch in Cholinergic Mechanisms of Modulation in the Medial Nucleus of the Trapezoid Body.J Neurosci. 2024 Feb 21;44(8):e0356232023. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0356-23.2023. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38383485 Free PMC article.
-
Sericin Improves Memory Impairment Via Activation of the PKA-CREB-BDNF Signaling Pathway and Suppression of Oxidative Stress in Ovariectomized Mice.Neurochem Res. 2024 Apr;49(4):1093-1104. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04094-5. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 38291264
-
What Can We Learn About Alzheimer's Disease from People with Down Syndrome?Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2025;69:197-226. doi: 10.1007/7854_2024_546. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39509049 Review.
References
-
- Hussain D, Shams W, Brake W. Estrogen and memory system bias in females across the lifespan. Transl Neurosci. 2014;5(1):35–50. doi: 10.2478/s13380-014-0209-7 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

