Climate drives coupled regime shifts across subtropical estuarine ecosystems
- PMID: 35939671
- PMCID: PMC9388116
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2121654119
Climate drives coupled regime shifts across subtropical estuarine ecosystems
Erratum in
-
Correction for Hesterberg et al., Climate drives coupled regime shifts across subtropical estuarine ecosystems.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Oct 4;119(40):e2215478119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2215478119. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36173952 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
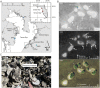
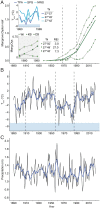
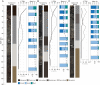
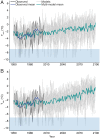
Ecological regime shifts are expected to increase this century as climate change propagates cascading effects across ecosystems with coupled elements. Here, we demonstrate that the climate-driven salt marsh-to-mangrove transition does not occur in isolation but is linked to lesser-known oyster reef-to-mangrove regime shifts through the provision of mangrove propagules. Using aerial imagery spanning 82 y, we found that 83% of oyster reefs without any initial mangrove cover fully converted to mangrove islands and that mean (± SD) time to conversion was 29.1 ± 9.6 y. In situ assessments of mangrove islands suggest substantial changes in ecosystem structure during conversion, while radiocarbon dates of underlying reef formation indicate that such transitions are abrupt relative to centuries-old reefs. Rapid transition occurred following release from freezes below the red mangrove (Rhizophora mangle) physiological tolerance limit (-7.3 °C) and after adjacent marsh-to-mangrove conversion. Additional nonclimate-mediated drivers of ecosystem change were also identified, including oyster reef exposure to wind-driven waves. Coupling of regime shifts arises from the growing supply of mangrove propagules from preceding and adjacent marsh-to-mangrove conversion. Climate projections near the mangrove range limit on the Gulf coast of Florida suggest that regime shifts will begin to transform subtropical estuaries by 2070 if propagule supply keeps pace with predicted warming. Although it will become increasingly difficult to maintain extant oyster habitat with tropicalization, restoring oyster reefs in high-exposure settings or active removal of mangrove seedlings could slow the coupled impacts of climate change shown here.
Keywords: Crassostrea virginica; climate change; historical ecology; mangrove; oyster reef.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Scheffer M., Carpenter S. R., Catastrophic regime shifts in ecosystems: Linking theory to observation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 18, 648–656 (2003).
-
- Biggs R., Peterson G., Rocha J., The Regime Shifts Database: A framework for analyzing regime shifts in social-ecological systems. Ecol. Soc. 23, art9 (2018).
-
- Barnosky A. D., et al. , Approaching a state shift in Earth’s biosphere. Nature 486, 52–58 (2012). - PubMed
-
- van Nes E. H., et al. , What do you mean, ‘tipping point’? Trends Ecol. Evol. 31, 902–904 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Graham N. A. J., et al. , Managing resilience to reverse phase shifts in coral reefs. Front. Ecol. Environ. 11, 541–548 (2013).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

