Protocol and baseline characteristics for a community health worker-led hypertension and diabetes management program for South Asians in Atlanta: The DREAM Atlanta study
- PMID: 35940551
- PMCID: PMC9708117
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cct.2022.106864
Protocol and baseline characteristics for a community health worker-led hypertension and diabetes management program for South Asians in Atlanta: The DREAM Atlanta study
Abstract
Background: South Asians are disproportionately affected by type 2 diabetes (DMII) and comorbid hypertension (HTN). Community health worker (CHW) interventions have been shown to improve chronic disease outcomes, yet few have been tailored for South Asians. This paper describes the study protocol and baseline characteristics of an evidence-based CHW intervention to improve blood pressure (BP) control among South Asian adults with diabetes and comorbid HTN in Atlanta, GA.
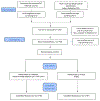
Methods: A total of 195 South Asian adults were randomized to treatment and control groups, and of these 190 completed baseline surveys (97 treatment group and 93 control group). The treatment group receives five group education sessions on DMII and HTN management and two one-on-one goal setting sessions.
Measures: Primary outcomes include feasibility, acceptability, and BP control (systolic blood pressure [SBP] <130 and diastolic blood pressure [DBP] <80). Secondary outcomes included changes in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), weight, diabetes self-efficacy, diet, and physical activity.
Baseline results: Of the enrolled sample, 56% are female and mean age is 56.0 (±11.7). All participants are foreign-born. Mean SBP was 139.2 ± 4.3 and mean DBP was 84.7 ± 9.5. Intervention outcomes are measured at baseline and 6-month endpoint for both study groups.
Conclusions: To our knowledge, this study is the first to document the efficacy of a HTN and DMII management intervention among South Asian adults in Atlanta, GA. Future findings of the submitted protocol will fill an important gap on the translation and adaption of evidence-based interventions that have relevance to immigrant and minority populations.
Clinical trials registration: NCT04263311.
Keywords: Community-based research; Diabetes; Hypertension; Immigrant health.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Culturally Adapted, Telehealth, Community Health Worker Intervention on Blood Pressure Control among South Asian Immigrants with Type II Diabetes: Results from the DREAM Atlanta Intervention.J Gen Intern Med. 2024 Mar;39(4):529-539. doi: 10.1007/s11606-023-08443-6. Epub 2023 Oct 16. J Gen Intern Med. 2024. PMID: 37845588 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Implementation of a multi-level community-clinical linkage intervention to improve glycemic control among south Asian patients with uncontrolled diabetes: study protocol of the DREAM initiative.BMC Endocr Disord. 2021 Nov 23;21(1):233. doi: 10.1186/s12902-021-00885-5. BMC Endocr Disord. 2021. PMID: 34814899 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Protocol for the DREAM Project (Diabetes Research, Education, and Action for Minorities): a randomized trial of a community health worker intervention to improve diabetic management and control among Bangladeshi adults in NYC.BMC Public Health. 2014 Feb 18;14:177. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-177. BMC Public Health. 2014. PMID: 24548534 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Community Diabetes Education (CoDE) for uninsured Mexican Americans: a randomized controlled trial of a culturally tailored diabetes education and management program led by a community health worker.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013 Apr;100(1):19-28. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2013.01.027. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013. PMID: 23453178 Review.
-
Effects of dietary and physical activity interventions on the risk of type 2 diabetes in South Asians: meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised controlled trials.Diabetologia. 2019 Aug;62(8):1337-1348. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-4905-2. Epub 2019 Jun 15. Diabetologia. 2019. PMID: 31201437 Review.
Cited by
-
Addressing Hypertension and Diabetes through Community-Engaged Systems (ANDES) in Puno, Peru: rationale and study protocol for a hybrid type 2 effectiveness and implementation randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2024 Nov 9;25(1):747. doi: 10.1186/s13063-024-08586-9. Trials. 2024. PMID: 39516847 Free PMC article.
-
A Culturally Adapted, Telehealth, Community Health Worker Intervention on Blood Pressure Control among South Asian Immigrants with Type II Diabetes: Results from the DREAM Atlanta Intervention.J Gen Intern Med. 2024 Mar;39(4):529-539. doi: 10.1007/s11606-023-08443-6. Epub 2023 Oct 16. J Gen Intern Med. 2024. PMID: 37845588 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sociodemographic and behavioral factors associated with diet quality among low-income community health center patients with hypertension.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 13;20(1):e0299781. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299781. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39804922 Free PMC article.
-
Unsung heroes in health education and promotion: How Community Health Workers contribute to hypertension management.Front Public Health. 2023 Feb 23;11:1088236. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1088236. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36908415 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shih M, et al., Stemming the tide: rising diabetes prevalence and ethnic subgroup variation among Asians in Los Angeles County. Prev Med, 2014. 63: p. 90–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous