Tracking Mental Wellbeing of Dutch Adolescents During the First Year of the COVID-19 Lockdown: A Longitudinal Study
- PMID: 35941018
- PMCID: PMC9217158
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2022.06.006
Tracking Mental Wellbeing of Dutch Adolescents During the First Year of the COVID-19 Lockdown: A Longitudinal Study
Abstract
Purpose: Adolescents might be susceptible to the effects of the COVID-19 lockdown. We assessed changes in mental wellbeing throughout the first year of the pandemic and compared these with prepandemic levels.
Methods: This five-wave prospective study among Dutch adolescents aged 12-17 years used data collected before the pandemic (n = 224) (T0), in May (T1), July (T2), and October 2020 (T3), and in February 2021 (T4). Generalized estimating equations were used to assess the association between stringency of the lockdown with mental wellbeing.
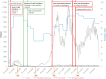
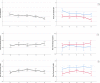
Results: Adolescents had a lower life satisfaction during the first full lockdown (T1) [adjusted β: -0.36, 95% confidence interval (CI): -0.58 to -0.13], during the partial lockdown (T3) (adjusted β: -0.37, 95% CI: -0.63 to -0.12), and during the second full lockdown (T4) (adjusted β: -0.79, 95% CI: -1.07 to -0.52) compared to before the pandemic (T0). Adolescents reported more internalizing symptoms during only the second full lockdown (T4) (adjusted β: 2.58, 95% CI: 0.41-4.75). During the pandemic [at T1 (adjusted β: 0.29, 95% CI: 0.20-0.38), T2 (adjusted β: 0.36, 95% CI: 0.26-0.46), T3 (adjusted β: 0.33, 95% CI: 0.22-0.45), and T4 (adjusted β: 0.20, 95% CI: 0.07-0.34)], adolescents reported a better psychosomatic health, partly attributable to less trouble falling asleep (p < .01).
Discussion: The COVID-19 lockdown measures have had both a negative and positive impact on mental wellbeing of Dutch adolescents. However, mental wellbeing was most impacted during the second full lockdown compared to before the pandemic.
Keywords: Adolescent; COVID-19 pandemic; Mental wellbeing.
Copyright © 2022 Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Haug N., Geyrhofer L., Londei A., et al. Ranking the effectiveness of worldwide COVID-19 government interventions. Nat Hum Behav. 2020;4:1303–1312. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organisation Q&A on coronaviruses (COVID-19). World health Organization. 2020. www.who.int Available at:
-
- Kessler R.C., Berglund P., Demler O., et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the national comorbidity survey replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:593–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

