A neural circuit for wind-guided olfactory navigation
- PMID: 35941114
- PMCID: PMC9360402
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-32247-7
A neural circuit for wind-guided olfactory navigation
Abstract
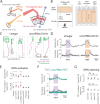
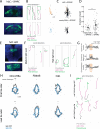
To navigate towards a food source, animals frequently combine odor cues about source identity with wind direction cues about source location. Where and how these two cues are integrated to support navigation is unclear. Here we describe a pathway to the Drosophila fan-shaped body that encodes attractive odor and promotes upwind navigation. We show that neurons throughout this pathway encode odor, but not wind direction. Using connectomics, we identify fan-shaped body local neurons called h∆C that receive input from this odor pathway and a previously described wind pathway. We show that h∆C neurons exhibit odor-gated, wind direction-tuned activity, that sparse activation of h∆C neurons promotes navigation in a reproducible direction, and that h∆C activity is required for persistent upwind orientation during odor. Based on connectome data, we develop a computational model showing how h∆C activity can promote navigation towards a goal such as an upwind odor source. Our results suggest that odor and wind cues are processed by separate pathways and integrated within the fan-shaped body to support goal-directed navigation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Murlis J, Elkinton JS, Carde RT. Odor plumes and how insects use them. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1992;37:505–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.37.010192.002445. - DOI
-
- Crimaldi JP, Koseff JR. High-resolution measurements of the spatial and temporal scalar structure of a turbulent plume. Exp. Fluids. 2001;31:90–102. doi: 10.1007/s003480000263. - DOI
-
- Webster DR, Weissburg MJ. Chemosensory guidance cues in a turbulent chemical odor plume. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001;46:1034–1047. doi: 10.4319/lo.2001.46.5.1034. - DOI
-
- Celani A, Villermaux E, Vergassola M. Odor landscapes in turbulent environments. Phys. Rev. X. 2014;4:041015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

