Identification of activity-induced Egr3-dependent genes reveals genes associated with DNA damage response and schizophrenia
- PMID: 35941129
- PMCID: PMC9360026
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-022-02069-8
Identification of activity-induced Egr3-dependent genes reveals genes associated with DNA damage response and schizophrenia
Abstract
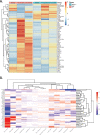
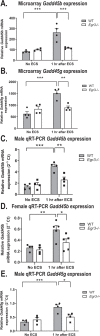
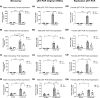
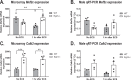
Bioinformatics and network studies have identified the immediate early gene transcription factor early growth response 3 (EGR3) as a master regulator of genes differentially expressed in the brains of patients with neuropsychiatric illnesses ranging from schizophrenia and bipolar disorder to Alzheimer's disease. However, few studies have identified and validated Egr3-dependent genes in the mammalian brain. We have previously shown that Egr3 is required for stress-responsive behavior, memory, and hippocampal long-term depression in mice. To identify Egr3-dependent genes that may regulate these processes, we conducted an expression microarray on hippocampi from wildtype (WT) and Egr3-/- mice following electroconvulsive seizure (ECS), a stimulus that induces maximal expression of immediate early genes including Egr3. We identified 69 genes that were differentially expressed between WT and Egr3-/- mice one hour following ECS. Bioinformatic analyses showed that many of these are altered in, or associated with, schizophrenia, including Mef2c and Calb2. Enrichr pathway analysis revealed the GADD45 (growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible) family (Gadd45b, Gadd45g) as a leading group of differentially expressed genes. Together with differentially expressed genes in the AP-1 transcription factor family genes (Fos, Fosb), and the centromere organization protein Cenpa, these results revealed that Egr3 is required for activity-dependent expression of genes involved in the DNA damage response. Our findings show that EGR3 is critical for the expression of genes that are mis-expressed in schizophrenia and reveal a novel requirement for EGR3 in the expression of genes involved in activity-induced DNA damage response.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Pfaffenseller B, da Silva Magalhaes PV, De Bastiani MA, Castro MA, Gallitano AL, Kapczinski F, et al. Differential expression of transcriptional regulatory units in the prefrontal cortex of patients with bipolar disorder: potential role of early growth response gene 3. Transl Psychiatry. 2016;6:e805. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.78. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

