Synaptosome microRNAs regulate synapse functions in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 35941185
- PMCID: PMC9359989
- DOI: 10.1038/s41525-022-00319-8
Synaptosome microRNAs regulate synapse functions in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
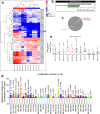
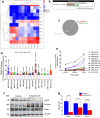
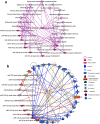
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are found in nerve terminals, synaptic vesicles, and synaptosomes, but it is unclear whether synaptic and cytosolic miRNA populations differ in Alzheimer's disease (AD) or if synaptosomal miRNAs affect AD synapse activity. To address these questions, we generated synaptosomes and cytosolic fractions from postmortem brains of AD and unaffected control (UC) samples and analyzed them using a global Affymetrix miRNAs microarray platform. A group of miRNAs significantly differed (P < 0.0001) with high fold changes variance (+/- >200-fold) in their expressions in different comparisons: (1) UC synaptosome vs UC cytosol, (2) AD synaptosomes vs AD cytosol, (3) AD cytosol vs UC cytosol, and (4) AD synaptosomes vs UC synaptosomes. MiRNAs data analysis revealed that some potential miRNAs were consistently different across sample groups. These differentially expressed miRNAs were further validated using AD postmortem brains, brains of APP transgenic (Tg2576), Tau transgenic (P301L), and wild-type mice. The miR-501-3p, miR-502-3p, and miR-877-5p were identified as potential synaptosomal miRNAs upregulated with disease progression based on AD Braak stages. Gene Ontology Enrichment and Ingenuity Pathway Analysis of synaptosomal miRNAs showed the involvement of miRNAs in nervous system development, cell junction organization, synapse assembly formation, and function of GABAergic synapse. This is the first description of synaptic versus cytosolic miRNAs in AD and their significance in synapse function.
© 2022. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors would like to inform that the authors filed a patent on “Synaptosomal miRNAs and Synapse Functions in Alzheimer’s Disease” TTU Ref. No. 2022-016, U.S. Provisional Pat. App. No. 63/332,866 on April 20, 2022 related to the contents of this manuscript.
Figures



References
-
- Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 17, 327–406 (2021). - PubMed
Grants and funding
- AG072973/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | Center for Scientific Review (NIH Center for Scientific Review)
- K99AG65645/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | Center for Scientific Review (NIH Center for Scientific Review)
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AG065645/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG076202/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG051086/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | Center for Scientific Review (NIH Center for Scientific Review)
- R56 AG072810/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG069333/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | Center for Scientific Review (NIH Center for Scientific Review)
- R21 AG056007/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG051086/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AG065645/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG042804/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG074539/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

