Novel identification and modulation of the mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel in human myometrium
- PMID: 35941750
- PMCID: PMC9905381
- DOI: 10.1113/JP283299
Novel identification and modulation of the mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel in human myometrium
Abstract
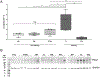
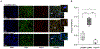
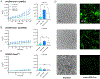
Approximately 10% of US births deliver preterm before 37 weeks of completed gestation. Premature infants are at risk for life-long debilitating morbidities and death, and spontaneous preterm labour explains 50% of preterm births. In all cases existing treatments are ineffective, and none are FDA approved. The mechanisms that initiate preterm labour are not well understood but may result from dysfunctional regulation of quiescence mechanisms. Human pregnancy is accompanied by large increases in blood flow, and the uterus must enlarge by orders of magnitude to accommodate the growing fetus. This mechanical strain suggests that stretch-activated channels may constitute a mechanism to explain gestational quiescence. Here we identify for the first time that Piezo1, a mechanosensitive cation channel, is present in the uterine smooth muscle and microvascular endothelium of pregnant myometrium. Piezo is downregulated during preterm labour, and stimulation of myometrial Piezo1 in an organ bath with the agonist Yoda1 relaxes the tissue in a dose-dependent fashion. Further, stimulation of Piezo1 while inhibiting protein kinase A, AKT, or endothelial nitric oxide synthase mutes the negative inotropic effects of Piezo1 activation, intimating that actions on the myocyte and endothelial nitric oxide signalling contribute to Piezo1-mediated contractile dynamics. Taken together, these data highlight the importance of stretch-activated channels in pregnancy maintenance and parturition, and identify Piezo1 as a tocolytic target of interest. KEY POINTS: Spontaneous preterm labour is a serious obstetric dilemma without a known cause or effective treatments. Piezo1 is a stretch-activated channel important to muscle contractile dynamics. Piezo1 is present in the myometrium and is dysregulated in women who experience preterm labour. Activation of Piezo1 by the agonist Yoda1 relaxes the myometrium in a dose-dependent fashion, indicating that Piezo1 modulation may have therapeutic benefits to treat preterm labour.
Keywords: Piezo1; mechanosensitive channels; myometrium; pregnancy; preterm labour; stretch-activated channels.
© 2022 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Physiological Society.
Figures
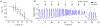

Comment in
-
Piezo1 activation by stretching of uterine myometrium supports pregnancy and prevents preterm labour.J Physiol. 2023 Feb;601(4):719-721. doi: 10.1113/JP283810. Epub 2022 Nov 5. J Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36266732 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Piezo1 overexpression in the uterus contributes to myometrium contraction and inflammation-associated preterm birth.J Transl Med. 2024 Dec 23;22(1):1140. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05978-y. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39716206 Free PMC article.
-
β3 Receptor Signaling in Pregnant Human Myometrium Suggests a Role for β3 Agonists as Tocolytics.Biomolecules. 2023 Jun 17;13(6):1005. doi: 10.3390/biom13061005. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37371585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Piezo1 activation by stretching of uterine myometrium supports pregnancy and prevents preterm labour.J Physiol. 2023 Feb;601(4):719-721. doi: 10.1113/JP283810. Epub 2022 Nov 5. J Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36266732 No abstract available.
-
Integration of endocrine and mechanical signals in the regulation of myometrial functions during pregnancy and labour.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009 May;144 Suppl 1:S2-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2009.02.044. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009. PMID: 19299064 Review.
-
Expression of stretch-activated two-pore potassium channels in human myometrium in pregnancy and labor.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 25;5(8):e12372. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012372. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20811500 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Piezo ion channels: long-sought-after mechanosensors mediating hypertension and hypertensive nephropathy.Hypertens Res. 2024 Oct;47(10):2786-2799. doi: 10.1038/s41440-024-01820-6. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Hypertens Res. 2024. PMID: 39103520 Review.
-
Ion-Channel Proteins in the Prepubertal Bitch Reproductive System: The Immunolocalization of ASIC2, ASIC4, and PIEZO2.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 5;26(9):4388. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094388. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362625 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulated TIMP1 facilitates and coordinates myometrial contraction by decreasing collagens and cell adhesive capacity during human labor.Mol Hum Reprod. 2023 Sep 30;29(10):gaad034. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaad034. Mol Hum Reprod. 2023. PMID: 37774003 Free PMC article.
-
β3 adrenergic receptor activation modulates connexin 43 activity to relax human myometrium.Cell Signal. 2023 Jun;106:110640. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110640. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Cell Signal. 2023. PMID: 36841274 Free PMC article.
-
Electrical wave generation and spatial organization in uterine tissue.J R Soc Interface. 2025 May;22(226):20240638. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2024.0638. Epub 2025 May 14. J R Soc Interface. 2025. PMID: 40364760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aaronson PI, Sarwar U, Gin S, Rockenbauch U, Connolly M, Tillet A, Watson S, Liu B & Tribe RM (2006). A role for voltage-gated, but not Ca 2+-activated, K + channels in regulating spontaneous contractile activity in myometrium from virgin and pregnant rats. Br J Pharmacol 147, 815–824. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abramson DJ & Reid DE (1955). Use of relaxin in treatment of threatened premature labor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 15 2, 206–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

