A Review on Recent Advances of Cerebral Palsy
- PMID: 35941906
- PMCID: PMC9356840
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2622310
A Review on Recent Advances of Cerebral Palsy
Abstract
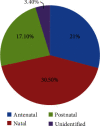
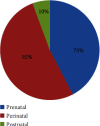
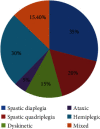
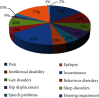
This narrative review summarizes the latest advances in cerebral palsy and identifies where more research is required. Several studies on cerebral palsy were analyzed to generate a general idea of the prevalence of, risk factors associated with, and classification of cerebral palsy (CP). Different classification systems used for the classification of CP on a functional basis were also analyzed. Diagnosis systems used along with the prevention techniques were discussed. State-of-the-art treatment strategies for CP were also analyzed. Statistical distribution was performed based on the selected studies. Prevalence was found to be 2-3/1000 lives; the factors that can be correlated are gestational age and birth weight. The risk factors identified were preconception, prenatal, perinatal, and postnatal categories. According to the evidence, CP is classified into spastic (80%), dyskinetic (15%), and ataxic (5%) forms. Diagnosis approaches were based on clinical investigation and neurological examinations that include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), biomarkers, and cranial ultrasound. The treatment procedures found were medical and surgical interventions, physiotherapy, occupational therapy, umbilical milking, nanomedicine, and stem cell therapy. Technological advancements in CP were also discussed. CP is the most common neuromotor disability with a prevalence of 2-3/1000 lives. The highest contributing risk factor is prematurity and being underweight. Several preventions and diagnostic techniques like MRI and ultrasound were being used. Treatment like cord blood treatment nanomedicine and stem cell therapy needs to be investigated further in the future to apply in clinical practice. Future studies are indicated in the context of technological advancements among cerebral palsy children.
Copyright © 2022 Sudip Paul et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Vitrikas K., Dalton H., Breish D. Cerebral palsy: an overview. American Family Physician . 2020;101(4):213–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

