Rapid Antigen Diagnostics as Frontline Testing in the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 35942171
- PMCID: PMC9349911
- DOI: 10.1002/smsc.202200009
Rapid Antigen Diagnostics as Frontline Testing in the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
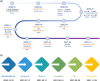
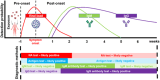
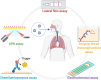
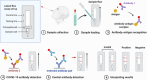
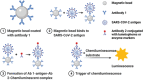
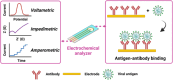
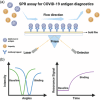
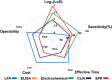
The ongoing global COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, has resulted in significant loss of life since December 2019. Timely and precise virus detection has been proven as an effective solution to reduce the spread of the virus and to track the epidemic. Rapid antigen diagnostics has played a significant role in the frontline of COVID-19 testing because of its convenience, low cost, and high accuracy. Herein, different types of recently innovated in-lab and commercial antigen diagnostic technologies with emphasis on the strengths and limitations of these technologies including the limit of detection, sensitivity, specificity, affordability, and usability are systematically reviewed. The perspectives of assay development are looked into.
Keywords: COVID-19; antigen tests; immnuoassays; in vitro diagnostics.
© 2022 The Authors. Small Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Laboratory-Based Resources for COVID-19 Diagnostics: Traditional Tools and Novel Technologies. A Perspective of Personalized Medicine.J Pers Med. 2021 Jan 13;11(1):42. doi: 10.3390/jpm11010042. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 33451039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Nanophotonic Label-Free Biosensors Can Contribute to Rapid and Massive Diagnostics of Respiratory Virus Infections: COVID-19 Case.ACS Sens. 2020 Sep 25;5(9):2663-2678. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.0c01180. Epub 2020 Aug 24. ACS Sens. 2020. PMID: 32786383 Review.
-
Comparative evaluation of RT-PCR and antigen-based rapid diagnostic tests (Ag-RDTs) for SARS-CoV-2 detection: performance, variant specificity, and clinical implications.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jun 4;12(6):e0007324. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00073-24. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38683014 Free PMC article.
-
[Evaluation of the Rapid Antigen Detection Kit with the Polymerase Chain Reaction for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Respiratory Samples].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2022 Apr;56(2):263-273. doi: 10.5578/mb.20229806. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2022. PMID: 35477229 Turkish.
-
Molecular Diagnostic Tools for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2.Int Rev Immunol. 2021;40(1-2):143-156. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2020.1871477. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Int Rev Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33439059 Review.
Cited by
-
A semi-quantitative upconversion nanoparticle-based immunochromatographic assay for SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection.Front Microbiol. 2023 Dec 11;14:1289682. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1289682. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38149276 Free PMC article.
-
Proof-of-Concept: Smartphone- and Cloud-Based Artificial Intelligence Quantitative Analysis System (SCAISY) for SARS-CoV-2-Specific IgG Antibody Lateral Flow Assays.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 5;13(6):623. doi: 10.3390/bios13060623. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37366988 Free PMC article.
-
Public's Willingness to Perform COVID-19 Self-Testing During the Transition to the Endemic Phase in Malaysia - A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Study.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2023 Nov 21;16:2505-2519. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S439530. eCollection 2023. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2023. PMID: 38024502 Free PMC article.
-
A single domain antibody-based Luminex assay for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical samples.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 13;15:1446095. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1446095. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39192985 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
