SMAD4 and TGFβ are architects of inverse genetic programs during fate determination of antiviral CTLs
- PMID: 35942952
- PMCID: PMC9402230
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.76457
SMAD4 and TGFβ are architects of inverse genetic programs during fate determination of antiviral CTLs
Abstract
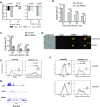
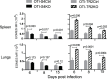
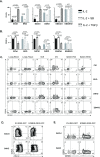
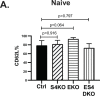
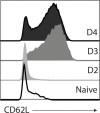
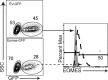
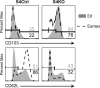
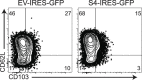
Transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) is an important differentiation factor for cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and alters the expression levels of several of homing receptors during infection. SMAD4 is part of the canonical signaling network used by members of the transforming growth factor family. For this study, genetically modified mice were used to determine how SMAD4 and TGFβ receptor II (TGFβRII) participate in transcriptional programming of pathogen-specific CTLs. We show that these molecules are essential components of opposing signaling mechanisms, and cooperatively regulate a collection of genes that determine whether specialized populations of pathogen-specific CTLs circulate around the body, or settle in peripheral tissues. TGFβ uses a canonical SMAD-dependent signaling pathway to downregulate Eomesodermin (EOMES), KLRG1, and CD62L, while CD103 is induced. Conversely, in vivo and in vitro data show that EOMES, KLRG1, CX3CR1, and CD62L are positively regulated via SMAD4, while CD103 and Hobit are downregulated. Intravascular staining also shows that signaling via SMAD4 promotes formation of long-lived terminally differentiated CTLs that localize in the vasculature. Our data show that inflammatory molecules play a key role in lineage determination of pathogen-specific CTLs, and use SMAD-dependent signaling to alter the expression levels of multiple homing receptors and transcription factors with known functions during memory formation.
Keywords: CD8 T cell differentiation; CD8 T cells; CD8 memory; SMAD4; TGFβ; cytotoxic T lymphocyte; immunology; inflammation; influenza a virus; listeria monocytogenes; mouse; respiratory virus.
© 2022, Chandiran et al.
Conflict of interest statement
KC, JS, YH, EJ, ZU, JL, BM, SK, LC No competing interests declared
Figures

References
-
- Cao J, Zhang X, Wang Q, Qiu G, Hou C, Wang J, Cheng Q, Lan Y, Han H, Shen H, Zhang Y, Yang X, Shen B, Zhang J. Smad4 represses the generation of memory-precursor effector T cells but is required for the differentiation of central memory T cells. Cell Death & Disease. 2015;6:e1984. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.337. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang JT, Ciocca ML, Kinjyo I, Palanivel VR, McClurkin CE, Dejong CS, Mooney EC, Kim JS, Steinel NC, Oliaro J, Yin CC, Florea BI, Overkleeft HS, Berg LJ, Russell SM, Koretzky GA, Jordan MS, Reiner SL. Asymmetric proteasome segregation as a mechanism for unequal partitioning of the transcription factor T-bet during T lymphocyte division. Immunity. 2011;34:492–504. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.03.017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

