The Therapeutic Significance of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in COVID-19 Acute Pulmonary Respiratory Disease
- PMID: 35943071
- PMCID: PMC9524499
- DOI: 10.5152/TurkThoracJ.2022.21302
The Therapeutic Significance of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in COVID-19 Acute Pulmonary Respiratory Disease
Abstract
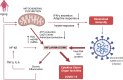
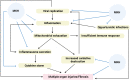
The coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus-2 continues its effects around the world with its new variants. Coronavirus disease 2019 infection may continue with a post-coronavirus disease period, which is characterized by high morbidity apart from the acute and subacute phases. Host immune response quality and inflammasome-induced uncontrollable inflammatory response take a role together in the pathogenesis of severe acute respiratory syndrome-related corona- virus-2 infection. Therefore, treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus-2 infection should basically include 3 measures: Viral replication, inflammation, and tissue damage control. Today, there is no effective therapy to control these points. At this point, preclinical studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cells can control inflammatory reactions and lung damage through both immune regulation and inflammasome control. Subsequently, controlled clinical studies on severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus-2 infection confirm their ability, indicating that mesenchymal stem cells may be a safe treatment option while reducing severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus-2-related morbidity and mortality. On the other hand, post-coronavirus syndrome is as important as acute coronavirus syndrome, it is a picture that can cause morbidity and mortality. Mesenchymal stem cell application can prevent the development of post-coronavirus syndrome through the mechanism of an inflammasome. However, there is no study that analyzes the effects of current treatments using mesenchymal stem cells in the post-coronavirus disease period, and that tests the use of mesenchymal stem cells when post-coronavirus syndrome develops. In this respect, studies that test the efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the post-coronavirus disease period are certainly needed.
Figures
References
-
- Çelik D, Köse Ş. Erişkinlerde COVID-19: Klinik Bulgular. Tepecik Eğit Araşt Hast Derg. 2020;30(Ek sayı):43 8.
-
- Baykal B. Mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of various diseases. J Stem Cell Res Med. 2016;1(2). 10.15761/JSCRM.1000110) - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
