Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare Competition (TEKNOFEST-2021): Stroke Data Set
- PMID: 35943079
- PMCID: PMC9797774
- DOI: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2022.22096
Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare Competition (TEKNOFEST-2021): Stroke Data Set
Abstract
Objective: The artificial intelligence competition in healthcare was organized for the first time at the annual aviation, space, and technology festival (TEKNOFEST), Istanbul/Türkiye, in September 2021. In this article, the data set preparation and competition processes were explained in detail; the anonymized and annotated data set is also provided via official website for further research.
Materials and methods: Data set recorded over the period covering 2019 and 2020 were centrally screened from the e-Pulse and Teleradiology System of the Republic of Türkiye, Ministry of Health using various codes and filtering criteria. The data set was anonymized. The data set was prepared, pooled, curated, and annotated by 7 radiologists. The training data set was shared with the teams via a dedicated file transfer protocol server, which could be accessed using private usernames and passwords given to the teams under a nondisclosure agreement signed by the representative of each team.
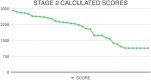
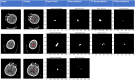
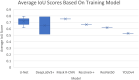
Results: The competition consisted of 2 stages. In the first stage, teams were given 192 digital imaging and communications in medicine images that belong to 1 of 3 possible categories namely, hemorrhage, ischemic, or non-stroke. Teams were asked to classify each image as either stroke present or absent. In the second stage of the competition, qualifying 36 teams were given 97 digital imaging and communications in medicine images that contained hemorrhage, ischemia, or both lesions. Among the employed methods, Unet and DeepLabv3 were the most frequently observed ones.
Conclusion: Artificial intelligence competitions in healthcare offer good opportunities to collect data reflecting various cases and problems. Especially, annotated data set by domain experts is more valuable.
Figures





References
-
- Aydoğan A, Türk Havacılık AD, Faaliyetlerinin Gelişim FVH. Süreci. Uluslararası Tarih Araştırmaları Derg. 2020;4(2):69 81.
-
- TEKNOFEST Official Website; 2021. Available at: https://teknofest.org/tr/.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
