In Vitro Susceptibility Testing of Eravacycline against Nontuberculous Mycobacteria
- PMID: 35943269
- PMCID: PMC9487454
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.00689-22
In Vitro Susceptibility Testing of Eravacycline against Nontuberculous Mycobacteria
Erratum in
-
Erratum for Brown-Elliott and Wallace, "In Vitro Susceptibility Testing of Eravacycline against Nontuberculous Mycobacteria".Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022 Nov 15;66(11):e0130422. doi: 10.1128/aac.01304-22. Epub 2022 Oct 18. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022. PMID: 36255269 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
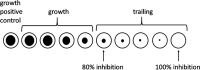
Nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) infections are increasing worldwide. Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) and the M. abscessus species are the most commonly cultured NTM and treatment options are limited, especially for the M. abscessus species. In this study, the in vitro activity of eravacycline, a new tetracycline derivative, was tested against 110 clinical isolates of NTM. MIC testing was performed as recommended by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute against 60 isolates of rapidly growing mycobacteria (RGM), of which ~70% were tetracycline resistant. These included M. abscessus subsp. abscessus (8 isolates), M. abscessus subsp. massiliense (5), M. chelonae (10), M. immunogenum (3), M. fortuitum group (20) including 12 doxycycline-resistant isolates, and M. mucogenicum group (10) including three doxycycline-resistant isolates. Due to trailing, eravacycline MICs were read at 80% and 100% inhibition. Eravacycline was active against all RGM species, with MIC50 ranges of ≤0.015 to 0.5 and ≤0.015 to 0.12 μg/mL for 100% and 80% inhibition, respectively. For M. abscessus subsp. abscessus, MIC50 values were 0.12 and 0.03 μg/mL with 100% and 80% inhibition, respectively. MICs for tigecycline were generally within 1 to 2 dilutions of the 100%-inhibition eravacycline MIC values. Fifty isolates of slowly growing mycobacteria (SGM) species, including 16 isolates of MAC, were also tested. While there was no trailing observed in most SGM, the eravacycline MICs were higher (MIC range of >8 μg/mL), except for M. kansasii and M. marinum which had MIC50 values of 1 μg/mL. This study supports further evaluation of eravacycline, including clinical trials for the development of RGM treatment regimens, especially for M. abscessus.
Keywords: eravacycline; nontuberculous mycobacteria; susceptibility.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare a conflict of interest. The authors received partial funding for this study from Tetraphase Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In Vitro Antimicrobial Activities of Tigecycline, Eravacycline, Omadacycline, and Sarecycline against Rapidly Growing Mycobacteria.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0323822. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03238-22. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36475850 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Susceptibility Testing of Omadacycline against Nontuberculous Mycobacteria.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Feb 17;65(3):e01947-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01947-20. Print 2021 Feb 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33288634 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of In Vitro Susceptibility of Delafloxacin with Ciprofloxacin, Moxifloxacin, and Other Comparator Antimicrobials against Isolates of Nontuberculous Mycobacteria.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Jun 17;65(7):e0007921. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00079-21. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33846136 Free PMC article.
-
The treatment of rapidly growing mycobacterial infections.Clin Chest Med. 2015 Mar;36(1):67-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2014.10.004. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Clin Chest Med. 2015. PMID: 25676520 Review.
-
An overview of pulmonary infections due to rapidly growing mycobacteria in South Asia and impressions from a subtropical region.Int J Mycobacteriol. 2020 Jan-Mar;9(1):62-70. doi: 10.4103/ijmy.ijmy_179_19. Int J Mycobacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32474491 Review.
Cited by
-
Third-Generation Tetracyclines: Current Knowledge and Therapeutic Potential.Biomolecules. 2024 Jun 30;14(7):783. doi: 10.3390/biom14070783. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tigecycline pharmacodynamics in the hollow fiber system of Mycobacterium avium-complex lung disease, and the utility of MICs and time-kill studies in drug development.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Aug 1:2025.07.29.667481. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.29.667481. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40766539 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Development of tetracycline analogues with increased aqueous stability for the treatment of mycobacterial infections.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2025 Jan;150:102592. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2024.102592. Epub 2024 Dec 13. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2025. PMID: 39708619 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for treating infections caused by non-tubercular mycobacteria: a narrative review from the study group on mycobacteria of the Italian Society of Infectious Diseases and Tropical Medicine.Infection. 2024 Jun;52(3):737-765. doi: 10.1007/s15010-024-02183-3. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Infection. 2024. PMID: 38329686 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

