Usefulness of ultrasound in the diagnosis of crystal deposition diseases
- PMID: 35943456
- PMCID: PMC11664834
- DOI: 10.5152/eurjrheum.2022.20129
Usefulness of ultrasound in the diagnosis of crystal deposition diseases
Abstract
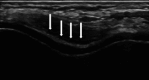
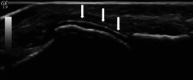
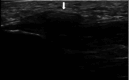
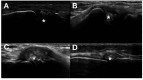
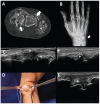
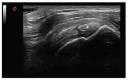
Gout and calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition disease (CPPD) are common forms of inflammatory arthritis whose prevalence has increased in recent years. Although the identification of monosodium urate crystals (MSU) and calcium pyrophosphate crystals (CPP) in synovial fluid (SF) by polarized light microscopy are the gold standard for diagnosing these diseases, SF analysis is not always available. An early diagnosis and specific treatment, especially in gout, allows avoiding irreversible structural damage, comorbidities, and a severe impact on the quality of life of patients. Musculoskeletal ultrasound (US) is a noninvasive tool that allows detecting aggregates of microcrystals at multiple anatomical sites and helps to establish a specific diagnosis. The objective of this review is to evaluate the applications of US in the diagnosis and clinical management of the main microcrystalline arthropathies. The US has helped improve our understanding of the natural history of the disease, due to its ability to visualize not only soft tissue inflammation and structural damage, but also the characteristics of MSU and CPP crystal deposition. The anatomical sites of crystal deposition are also a key factor for differential diagnosis in different microcrystalline diseases. The US allows establishing an early diagnosis, especially in asymptomatic hyperuricemia, to discriminate with other inflammatory diseases, to assess the extent of microcrystalline deposition and their sensitivity to change after treatment. Given its increasing availability in clinical practice and strong evidence, US is a bedside imaging technique helping clinicians to improve diagnosis and therapy monitoring in their daily practice.
Figures
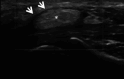
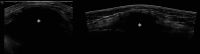
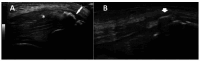
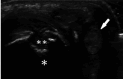

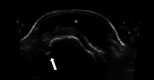
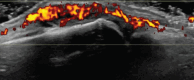
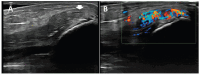
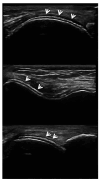

Similar articles
-
Synovial fluid analysis for the enhanced clinical diagnosis of crystal arthropathies in a tertiary care institution.Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Aug;40(8):3239-3246. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05610-0. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33598809
-
The added value of synovial fluid centrifugation for monosodium urate and calcium pyrophosphate crystal detection.Clin Rheumatol. 2017 Jul;36(7):1599-1605. doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3633-6. Epub 2017 Apr 19. Clin Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28424907
-
Crystal arthritides - gout and calcium pyrophosphate arthritis : Part 2: clinical features, diagnosis and differential diagnostics.Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2018 Jul;51(5):579-584. doi: 10.1007/s00391-017-1198-2. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2018. PMID: 28233118 Review. English.
-
"Crystal clear"-sonographic assessment of gout and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Dec;36(3):197-202. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2006.08.001. Epub 2006 Sep 29. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 17011611 Review.
-
Diff Quik staining method for detection and identification of monosodium urate and calcium pyrophosphate crystals in synovial fluids.Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Mar;60(3):194-8. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.3.194. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001. PMID: 11171677 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Study on the Diagnostic Value of Dual-Energy CT (DECT) Imaging in Patients With Gouty Arthritis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2024 Dec;27(12):e15431. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.15431. Int J Rheum Dis. 2024. PMID: 39618108 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bayat S, Baraf HSB, Rech J. Update on imaging in gout: Contrasting and comparing the role of dual-energy computed tomography to traditional diagnostic and monitoring techniques. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018;36(Suppl 114):53–60.. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
