Ultrasound-guided interventions in rheumatology
- PMID: 35943457
- PMCID: PMC11664835
- DOI: 10.5152/eurjrheum.2021.20233
Ultrasound-guided interventions in rheumatology
Abstract
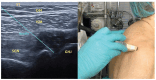
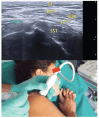
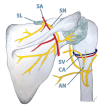
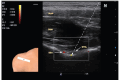
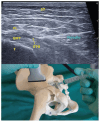
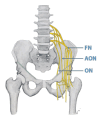
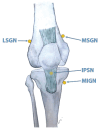
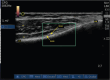
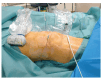
Over the last few years, percutaneous procedures have undergone great advances, thanks to the ultrasound (US) guidance, due to the technical improvements in the US field, combined with the greater availability, good portability, and reduced cost of US devices. The direct target visualization and the real-time imaging performance enabled by US-guidance account for an improved accuracy in needle placement in several rheumatology interventions. So, ultrasound-guided procedures contribute to several diagnostic or therapeutic procedures such as fluid aspiration or treatment instillations of common joints, tendons, and bursas. In clinical practice, this fact is especially important in the case of depth areas like the hip, small anatomical structures as tendon sheaths or nerves in tenosynovitis or nervous blocks, or complex anatomical structures like the spine's facet joints. The US-guide is an essential tool for performing diagnostic procedures as synovial biopsy. US can also be combined with other imaging techniques, like the establishment portal arthroscopy for instance. Compared to older blind procedures, US-guided injections are more accurate and safer, and they result in better clinical outcomes in terms of joints improvement in function and decreased risk of damages caused by needle misplacement. With the ultrasound guided treatment, we can avoid the instillation of therapeutic products outside the predetermined target, which may be sometimes potentially harmful. The aim of this article is to describe the main generalities of ultrasound-guided procedures in rheumatology, their main advantages and disadvantages, and their particularities in joints where they are most frequently used, such as the shoulder, hip, and knee.
Figures
References
-
- Hollander JL, Brown EM Jr, Jessar RA, Brown CY. Comparative effects of compound F (17-hy-droxycorticosterone) and cortisone injected locally into the rheumatoid arthritis joint. Ann Rheum Dis. 1951;10:473–476.. - PubMed
-
- Bianchi S, Zamorani P. US-guided interventional procedures. In Bianchi S, Martinolli C. (eds.): Ultrasound of the Musculoskeletal System. Berlin: Springer, 2007: 891–917..
-
- Park KD, Kim TK, Lee J, Lee WY, Ahn JK, Park Y. Palpation versus ultrasound-guided acromioclavicular joint intra-articular corticosteroid injections: A retrospective comparative clinical study. Pain Phys. 2015;18(4):333–341.. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
