High Expression of circ_0001821 Promoted Colorectal Cancer Progression Through miR-600/ISOC1 Axis
- PMID: 35943670
- PMCID: PMC9852123
- DOI: 10.1007/s10528-022-10262-z
High Expression of circ_0001821 Promoted Colorectal Cancer Progression Through miR-600/ISOC1 Axis
Abstract
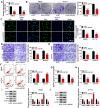
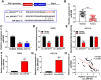
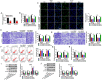
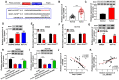
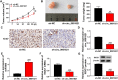
It has been reported that circRNAs play an important regulatory role in the progression of colorectal cancer (CRC). However, the molecular role of circ_0001821 in CRC development is unclear. In this study, we aimed to investigate the regulatory role and molecular mechanisms of circ_0001821 in CRC. Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR and western blot assays were used to detect the expression of circ_0001821, miR-600 and isochorismatase domain containing 1 (ISOC1) in CRC tissues as well as its cell lines. Colony formation assay and EDU assay were used to detect the proliferative capacity of cells. Transwell assay was used to assess cell migration and invasion ability. Flow cytometry was used to analyze cell apoptosis. ELISA was used to measure the glycolytic capacity of cells. Dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA pull-down assay were used to analyze the relationships between circ_0001821, miR-600 and ISOC1. Animal experimentation was used to validate the functional study of circ_0001821 in vivo. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) of Ki67 staining analysis was conducted to assess tumor growth. Circ_0001821 and ISOC1 were significantly increased in CRC tissues and its cell lines, and miR-600 was significantly decreased in CRC tissues and its cell lines. Silencing circ_0001821 inhibited cell proliferation, migration, invasion and glycolytic capacity, while inducing apoptosis. And it could inhibit tumor growth in vivo. Circ_0001821 could act as a sponge for miR-600 to regulate CRC processes. ISOC1 was identified as a downstream regulator of miR-600, also miR-600 could regulate the expression of ISOC1. In addition, circ_0001821 could regulate ISOC1 expression changes through miR-600. Mechanistically, either miR-600 inhibitor or overexpression of ISOC1 could reverse the effects of knockdown of circ_0001821 on cell biological properties. Circ_0001821 regulated the developmental process of CRC through miR-600/ISOC1 axis.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; ISOC1; circ_0001821; miR-600.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Circular RNA circ_0007142 regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion via miR-455-5p/SGK1 axis in colorectal cancer.Anticancer Drugs. 2021 Jan 1;32(1):22-33. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000992. Anticancer Drugs. 2021. PMID: 32889894
-
Circ_0007422 Knockdown Inhibits Tumor Property and Immune Escape of Colorectal Cancer by Decreasing PDL1 Expression in a miR-1256-Dependent Manner.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Sep;66(9):2606-2619. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-01040-2. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38253900
-
Hsa_circ_0000231 knockdown inhibits the glycolysis and progression of colorectal cancer cells by regulating miR-502-5p/MYO6 axis.World J Surg Oncol. 2020 Sep 29;18(1):255. doi: 10.1186/s12957-020-02033-0. World J Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32993655 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_0087862 promotes tumorigenesis and glycolysis in colorectal cancer by sponging miR-296-3p to regulate PGK1 expression.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Aug;248:154695. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154695. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37494801
-
Circular RNA (circ)_0053277 Contributes to Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth, Angiogenesis, Metastasis and Glycolysis.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Nov;66(11):3285-3299. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00936-3. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37917325
Cited by
-
Crosstalk between non-coding RNAs and programmed cell death in colorectal cancer: implications for targeted therapy.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2025 Jan 15;18(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13072-024-00560-8. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2025. PMID: 39810224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ge-SAND: an explainable deep learning-driven framework for disease risk prediction by uncovering complex genetic interactions in parallel.BMC Genomics. 2025 May 1;26(1):432. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11588-9. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40312319 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Driver Genes and miRNAs in Ovarian Cancer through an Integrated In-Silico Approach.Biology (Basel). 2023 Jan 26;12(2):192. doi: 10.3390/biology12020192. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonney GK, Chew CA, Lodge P, Hubbard J, Halazun KJ, Trunecka P, et al. Liver transplantation for non-resectable colorectal liver metastases: the International Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Association consensus guidelines. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;6(11):933–946. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00219-3. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

