Functional and biological heterogeneity of KRASQ61 mutations
- PMID: 35944066
- PMCID: PMC9534304
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.abn2694
Functional and biological heterogeneity of KRASQ61 mutations
Abstract
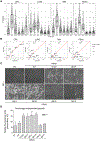
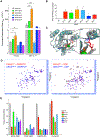
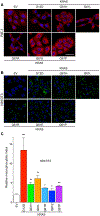
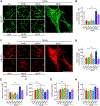
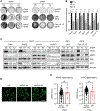
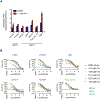
Missense mutations at the three hotspots in the guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) RAS-Gly12, Gly13, and Gln61 (commonly known as G12, G13, and Q61, respectively)-occur differentially among the three RAS isoforms. Q61 mutations in KRAS are infrequent and differ markedly in occurrence. Q61H is the predominant mutant (at 57%), followed by Q61R/L/K (collectively 40%), and Q61P and Q61E are the rarest (2 and 1%, respectively). Probability analysis suggested that mutational susceptibility to different DNA base changes cannot account for this distribution. Therefore, we investigated whether these frequencies might be explained by differences in the biochemical, structural, and biological properties of KRASQ61 mutants. Expression of KRASQ61 mutants in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts and RIE-1 epithelial cells caused various alterations in morphology, growth transformation, effector signaling, and metabolism. The relatively rare KRASQ61E mutant stimulated actin stress fiber formation, a phenotype distinct from that of KRASQ61H/R/L/P, which disrupted actin cytoskeletal organization. The crystal structure of KRASQ61E was unexpectedly similar to that of wild-type KRAS, a potential basis for its weak oncogenicity. KRASQ61H/L/R-mutant pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cell lines exhibited KRAS-dependent growth and, as observed with KRASG12-mutant PDAC, were susceptible to concurrent inhibition of ERK-MAPK signaling and of autophagy. Our results uncover phenotypic heterogeneity among KRASQ61 mutants and support the potential utility of therapeutic strategies that target KRASQ61 mutant-specific signaling and cellular output.
Figures

Comment in
-
Heterogeneity in RAS mutations: One size does not fit all.Sci Signal. 2022 Aug 9;15(746):eadc9816. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.adc9816. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Sci Signal. 2022. PMID: 35944067 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Papke B, Der CJ, Drugging RAS: Know the enemy. Science. 355, 1158–1163 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA042978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009156/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA213775/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016086/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA175747/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA199235/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM130457/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA071341/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA232372/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM134962/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA200313/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA203657/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA232113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA196510/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 CA243253/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

