The potency of common proinflammatory cytokines measurement for revealing the risk and severity of anxiety and depression in psoriasis patients
- PMID: 35944185
- PMCID: PMC9459285
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24643
The potency of common proinflammatory cytokines measurement for revealing the risk and severity of anxiety and depression in psoriasis patients
Abstract
Objective: Proinflammatory cytokines mediate anxiety and depression in various ways, such as immunity, inflammation, and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. This study intended to further explore the linkage of common proinflammatory cytokine levels with anxiety and depression in psoriasis patients.
Methods: Totally, 150 psoriasis patients and 50 healthy controls (HCs) were included; the serum samples were collected, then common proinflammatory cytokines were measured by ELISA. Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) was assessed.
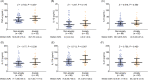
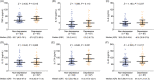
Results: HADS-anxiety (HADS-A) score, HADS-depression (HADS-D) score, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12, IL-17A, and IL-23 were all increased in psoriasis patients compared to HCs (all p < 0.05). In psoriasis patients, TNF-α (p = 0.001), IL-12 (p = 0.035), and IL-17A (p < 0.001), but not IL-1β (p = 0.255), IL-6 (p = 0.248), and IL-23 (p = 0.216), were positively linked to HADS-A score. Meanwhile, TNF-α (p = 0.007) and IL-17A (p = 0.007) were enhanced in psoriasis patients with anxiety in contrast to those without anxiety; whereas IL-1β (p = 0.178), IL-6 (p = 0.360), IL-12 (p = 0.239), and IL-23 (p = 0.450) were not different. TNF-α (p < 0.001), IL-1β (p = 0.013), Il-17A (p < 0.001), and IL-23 (p = 0.023), but not IL-6 (p = 0.143) and IL-12 (p = 0.158), were positively linked to HADS-D score. Concurrently, TNF-α (p = 0.015), IL-17A (p < 0.001), and IL-23 (p = 0.017) were climbed in psoriasis patients with depression by comparison to those without depression; whereas IL-1β (p = 0.113), IL-6 (p = 0.237), IL-12 (p = 0.660) did not differ.
Conclusion: TNF-α, IL-17A, and IL-23 increments reflect anabatic anxiety and depression in psoriasis patients, uncovering the potency of proinflammatory cytokines measurement for monitoring or even preventing psoriasis patients' anxiety and depression.
Keywords: anxiety; depression; hospital anxiety and depression scale; proinflammatory cytokines; psoriasis.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The relation of common inflammatory cytokines with anxiety and depression and their values in estimating cardiovascular outcomes in coronary heart disease patients.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Jun;36(6):e24404. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24404. Epub 2022 May 2. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35500142 Free PMC article.
-
Serum tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, and interleukin-17 relate to anxiety and depression risks to some extent in non-small cell lung cancer survivor.Clin Respir J. 2022 Feb;16(2):105-115. doi: 10.1111/crj.13457. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Clin Respir J. 2022. PMID: 34697903 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of common inflammatory cytokines with cognition impairment, anxiety, and depression in acute ischemic stroke patients.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2022 Feb 28;55:e11517. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2021e11517. eCollection 2022. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2022. PMID: 35239774 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokines, prostaglandins and nitric oxide in the regulation of stress-response systems.Pharmacol Rep. 2013;65(6):1655-62. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(13)71527-5. Pharmacol Rep. 2013. PMID: 24553014 Review.
-
Proinflammatory cytokines and neuropeptides in psoriasis, depression, and anxiety.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2025 Mar;241(3):e70019. doi: 10.1111/apha.70019. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2025. PMID: 39960105 Review.
Cited by
-
Elevated Specific Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Peripheral Circulation Indicate an Increased Risk of Anxiety and Depression in Rosacea.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jul 9;17:4443-4452. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S468773. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39006492 Free PMC article.
-
The Skin-Brain Axis in Psoriasis and Depression: Roles of Inflammation, Hormones, Neuroendocrine Pathways, Neuropeptides, and the Microbiome.Psoriasis (Auckl). 2025 Aug 18;15:411-428. doi: 10.2147/PTT.S535900. eCollection 2025. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2025. PMID: 40860250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychopathological Profile of Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis and Its Correlation to DLQI: Results from a Prospective, Monocentric Clinical Study.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 26;13(21):6424. doi: 10.3390/jcm13216424. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39518563 Free PMC article.
-
Early-life bisphenol A exposure causes neuronal pyroptosis in juvenile and adult male rats through the NF-κB/IL-1β/NLRP3/caspase-1 signaling pathway: exploration of age and dose as effective covariates using an in vivo and in silico modeling approach.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Apr;480(4):2301-2330. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05039-4. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 38941031 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Link Between Psoriasis and Depression-Update on Pathophysiology.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 10;26(6):2467. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062467. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141110 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

