Paclitaxel induces cognitive impairment via necroptosis, decreased synaptic plasticity and M1 polarisation of microglia
- PMID: 35944285
- PMCID: PMC9367659
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2108064
Paclitaxel induces cognitive impairment via necroptosis, decreased synaptic plasticity and M1 polarisation of microglia
Abstract
Context: Paclitaxel (PTX) leads to chemotherapy brain (chemo-brain) which is characterised by cognitive impairment. It has been reported that necroptosis is associated with cognitive impairment in some neurodegenerative diseases, but it is not clear whether it is related to the development of chemo-brain.
Objective: To investigate the role of necroptosis and related changes in PTX-induced cognitive impairment.
Materials and methods: C57bl/6n mice were randomly divided into five groups: control, vehicle, and different concentrations of PTX (6, 8, 10 mg/kg). Two additional groups received pre-treatment with Gdcl3 or PBS through Intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection before PTX-treatment. Cognitive function, necroptosis, synaptic plasticity and microglia polarisation were analysed.
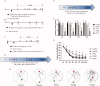
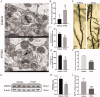
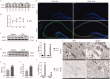
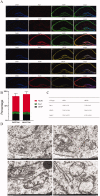
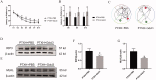
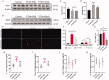
Results: PTX (10 mg/kg) induced significant cognitive impairment, accompanied by changes in synaptic plasticity, including decreased density of PSD95 (0.65-fold), BDNF (0.44-fold) and dendritic spines (0.57-fold). PTX induced necroptosis of 53.41% (RIP3) and 61.91% (MLKL) in hippocampal neurons, with high expression of RIP3 (1.58-fold) compared with the control group. MLKL (1.87-fold) exhibited the same trend, reaching a peak on the 14th day. The increased expression of iNOS (1.63-fold) and inflammatory factors such as TNF-α (1.85-fold) and IL-β (1.89-fold) compared to the control group suggests that M1 polarisation of microglia is involved in the process of cognitive impairment. Pre-treatment with Gdcl3 effectively reduced the number of microglia (0.50-fold), inhibited the release of TNF-α (0.73-fold) and IL-β (0.56-fold), and improved cognitive impairment.
Conclusion: We established a stable animal model of PTX-induced cognitive impairment and explored the underlying pathophysiological mechanism. These findings can guide the future treatment of chemo-brain.
Keywords: Central neurotoxicity; astrocytes; hippocampus; inflammatory factors; neuron.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Atarod D, Eskandari-Sedighi G, Pazhoohi F, Karimian S, Khajeloo M, Riazi G.. 2015. Microtubule dynamicity is more important than stability in memory formation: an in vivo study. J Mol Neurosci. 56(2):313–319. - PubMed
-
- Augusto-Oliveira M, Arrifano G, Takeda P, Lopes-Araújo A, Santos-Sacramento L, Anthony D, Verkhratsky A, Crespo-Lopez M.. 2020. Astroglia-specific contributions to the regulation of synapses, cognition and behaviour. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 118:331–357. - PubMed
-
- Bolaños J, Almeida A, Stewart V, Peuchen S, Land J, Clark J, Heales S.. 1997. Nitric oxide-mediated mitochondrial damage in the brain: mechanisms and implications for neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurochem. 68(6):2227–2240. - PubMed
-
- Boyette-Davis J, Fuchs P.. 2009. Differential effects of paclitaxel treatment on cognitive functioning and mechanical sensitivity. Neurosci Lett. 453(3):170–174. - PubMed
-
- Finke C, Prüss H, Heine J, Reuter S, Kopp U, Wegner F, Then Bergh F, Koch S, Jansen O, Münte T, et al. 2017. Evaluation of cognitive deficits and structural hippocampal damage in encephalitis with leucinerich, glioma-inactivated 1 antibodies. JAMA Neurol. 74:50–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
