Reduced field-of-view and multi-shot DWI acquisition techniques: Prospective evaluation of image quality and distortion reduction in prostate cancer imaging
- PMID: 35944809
- PMCID: PMC9523455
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2022.08.008
Reduced field-of-view and multi-shot DWI acquisition techniques: Prospective evaluation of image quality and distortion reduction in prostate cancer imaging
Abstract
Objectives: To prospectively compare image quality and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) quantification for reduced field-of-view (rFOV)- and multi-shot echo-planar imaging (msEPI)-based diffusion weighted imaging (DWI), using single-shot echo-planar-imaging (ssEPI) DWI as the reference.
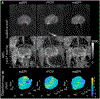
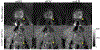
Methods: Under IRB approval and after informed consent, msEPI, rFOV, and ssEPI DWI acquisitions were prospectively added to clinical prostate MRI exams at 3.0 T. Image distortion was quantitatively evaluated by root-mean-squared displacement (dr.m.s.). Histogram-based quantitative ADC parameters were compared in a sub-set of patients for proven sites of prostate cancer and matched non-cancerous prostate. Three radiologists also independently evaluated the DWI sequences for subjective image quality and distortion/artifact on a 5-point Likert scale.
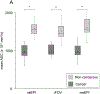
Results: Twenty-five patients were included (15 with proven sites of cancer). Average dr.m.s. demonstrated a small but statistically significant reduction in distortion for both rFOV and msEPI relative to ssEPI. Quantitative ADC parameters for prostate tumors demonstrated no significant difference across the 3 DWI acquisitions and each acquisition demonstrated a statistically significant decrease in mean ADC for tumor compared to normal prostate. Qualitative reader assessment demonstrated favorable image quality for rFOV and msEPI, more notable for msEPI.
Conclusions: rFOV and msEPI DWI techniques achieved reduction in image distortion, improvement in image quality, and maintained reproducible ADC quantification compared to the standard ssEPI.
Keywords: Diffusion weighted imaging; Echo planar imaging; Prostate cancer; image processing, computer-assisted; magnetic resonance imaging.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Fütterer JJ, Briganti A, De Visschere P, Emberton M, Giannarini G, Kirkham A, et al. Can Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Be Detected with Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging? A Systematic Review of the Literature. Eur Urol 2015;68:1045–1053. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.01.013. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

