Development and profiling of mGlu7 NAMs with a range of saturable inhibition of agonist responses in vitro
- PMID: 35944850
- PMCID: PMC10015594
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128923
Development and profiling of mGlu7 NAMs with a range of saturable inhibition of agonist responses in vitro
Abstract
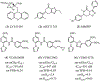
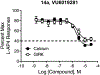
We describe here a series of metabotropic glutamate receptor 7 (mGlu7) negative allosteric modulators (NAMs) with a saturable range of activity in inhibiting responses to an orthosteric agonist in two distinct in vitro pharmacological assays. The range of inhibition among compounds in this scaffold provides highly structurally related ligands with differential degrees of receptor blockade that can be used to understand inhibitory efficacy profiles in native tissue or in vivo.
Keywords: Metabotropic glutamate receptor; Positive Allosteric modulator (PAM); Structure Activity Relationship (SAR); mGlu(7).
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
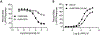
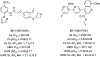
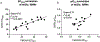



Similar articles
-
Structural determinants of allosteric antagonism at metabotropic glutamate receptor 2: mechanistic studies with new potent negative allosteric modulators.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;164(2b):521-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01409.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21470207 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of allosteric modulation: Exploring the binding kinetics of glutamate and other orthosteric ligands of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 2.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Sep;155:356-365. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.07.014. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30028996
-
Differential activity of mGlu7 allosteric modulators provides evidence for mGlu7/8 heterodimers at hippocampal Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses.J Biol Chem. 2022 Oct;298(10):102458. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102458. Epub 2022 Sep 5. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 36063995 Free PMC article.
-
Reprint of Pharmacological and molecular characterization of the positive allosteric modulators of metabotropic glutamate receptor 2.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Mar 15;115:115-127. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.08.040. Epub 2017 Feb 16. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28216000 Review.
-
Allosteric modulators of metabotropic glutamate receptors: lessons learnt from mGlu1, mGlu2 and mGlu5 potentiators and antagonists.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Nov;32(Pt 5):881-7. doi: 10.1042/BST0320881. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 15494040 Review.
Cited by
-
Profiling the Impact of mGlu7/Elfn1 Protein Interactions on the Pharmacology of mGlu7 Allosteric Modulators.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025 Aug 6;16(15):2872-2886. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5c00174. Epub 2025 Jul 21. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40689847 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Activity of Orthosteric Agonists and Allosteric Modulators at Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 7.Mol Pharmacol. 2023 Jul;104(1):17-27. doi: 10.1124/molpharm.123.000678. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Mol Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37105671 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

