Advances in Emerging Photonic Memristive and Memristive-Like Devices
- PMID: 35945187
- PMCID: PMC9534950
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202105577
Advances in Emerging Photonic Memristive and Memristive-Like Devices
Abstract
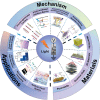
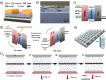
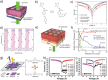
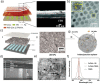
Possessing the merits of high efficiency, low consumption, and versatility, emerging photonic memristive and memristive-like devices exhibit an attractive future in constructing novel neuromorphic computing and miniaturized bionic electronic system. Recently, the potential of various emerging materials and structures for photonic memristive and memristive-like devices has attracted tremendous research efforts, generating various novel theories, mechanisms, and applications. Limited by the ambiguity of the mechanism and the reliability of the material, the development and commercialization of such devices are still rare and in their infancy. Therefore, a detailed and systematic review of photonic memristive and memristive-like devices is needed to further promote its development. In this review, the resistive switching mechanisms of photonic memristive and memristive-like devices are first elaborated. Then, a systematic investigation of the active materials, which induce a pivotal influence in the overall performance of photonic memristive and memristive-like devices, is highlighted and evaluated in various indicators. Finally, the recent advanced applications are summarized and discussed. In a word, it is believed that this review provides an extensive impact on many fields of photonic memristive and memristive-like devices, and lay a foundation for academic research and commercial applications.
Keywords: artificial visual system; brain-like computing; memristive-like behavior; memristors; photoelectric logic; photonic memristive devices; resistive switching.
© 2022 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Emerging Memristive Artificial Synapses and Neurons for Energy-Efficient Neuromorphic Computing.Adv Mater. 2020 Dec;32(51):e2004659. doi: 10.1002/adma.202004659. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Adv Mater. 2020. PMID: 33006204 Review.
-
Organic iontronic memristors for artificial synapses and bionic neuromorphic computing.Nanoscale. 2024 Jan 25;16(4):1471-1489. doi: 10.1039/d3nr06057h. Nanoscale. 2024. PMID: 38180037 Review.
-
Memristors Based on 2D Materials as an Artificial Synapse for Neuromorphic Electronics.Adv Mater. 2020 Dec;32(51):e2002092. doi: 10.1002/adma.202002092. Epub 2020 Sep 27. Adv Mater. 2020. PMID: 32985042 Review.
-
Recent Advances and Future Prospects for Memristive Materials, Devices, and Systems.ACS Nano. 2023 Jul 11;17(13):11994-12039. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c03505. Epub 2023 Jun 29. ACS Nano. 2023. PMID: 37382380 Review.
-
Interfacing Biology and Electronics with Memristive Materials.Adv Mater. 2023 Aug;35(32):e2210035. doi: 10.1002/adma.202210035. Epub 2023 Jun 29. Adv Mater. 2023. PMID: 36829290 Review.
Cited by
-
A memristive-photoconductive transduction methodology for accurately nondestructive memory readout.Light Sci Appl. 2024 Jul 23;13(1):175. doi: 10.1038/s41377-024-01519-w. Light Sci Appl. 2024. PMID: 39043644 Free PMC article.
-
Neuromorphic Computing via Fission-based Broadband Frequency Generation.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Dec;10(35):e2303835. doi: 10.1002/advs.202303835. Epub 2023 Oct 2. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37786262 Free PMC article.
-
Tailoring Classical Conditioning Behavior in TiO2 Nanowires: ZnO QDs-Based Optoelectronic Memristors for Neuromorphic Hardware.Nanomicro Lett. 2024 Feb 27;16(1):133. doi: 10.1007/s40820-024-01338-z. Nanomicro Lett. 2024. PMID: 38411720 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon Nanodots Memristor: An Emerging Candidate toward Artificial Biosynapse and Human Sensory Perception System.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Jun;10(16):e2207229. doi: 10.1002/advs.202207229. Epub 2023 Apr 18. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37072642 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yan X., Pei Y., Chen H., Zhao J., Zhou Z., Wang H., Zhang L., Wang J., Li X., Qin C., Wang G., Xiao Z., Zhao Q., Wang K., Li H., Ren D., Liu Q., Zhou H., Chen J., Zhou P., Adv. Mater. 2018, 31, 1805284. - PubMed
-
- Zidan M. A., Strachan J. P., Lu W. D., Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 22.
-
- Borghetti J., Snider G. S., Kuekes P. J., Yang J. J., Stewart D. R., Williams R. S., Nature 2010, 464, 873. - PubMed
-
- Yang H., Yang Q., He L., Wu X., Gao C., Zhang X., Shan L., Chen H., Guo T., Nano Res. 2021, 15, 386.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
