Synthesis of bioactive (1→6)-β-glucose branched poly-amido-saccharides that stimulate and induce M1 polarization in macrophages
- PMID: 35945224
- PMCID: PMC9363418
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-32346-5
Synthesis of bioactive (1→6)-β-glucose branched poly-amido-saccharides that stimulate and induce M1 polarization in macrophages
Abstract
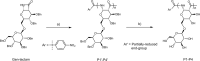
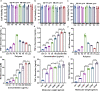
β-Glucans are of significant interest due to their potent antitumor and immunomodulatory activities. Nevertheless, the difficulty in purification, structural heterogenicity, and limited solubility impede the development of structure-property relationships and translation to therapeutic applications. Here, we report the synthesis of a new class of (1→6)-β-glucose-branched poly-amido-saccharides (PASs) as β-glucan mimetics by ring-opening polymerization of a gentiobiose-based disaccharide β-lactam and its copolymerization with a glucose-based β-lactam, followed by post-polymerization deprotection. The molecular weight (Mn) and frequency of branching (FB) of PASs is readily tuned by adjusting monomer-to-initiator ratio and mole fraction of gentiobiose-lactam in copolymerization. Branched PASs stimulate mouse macrophages, and enhance production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in a FB-, dose-, and Mn-dependent manner. The stimulation proceeds via the activation of NF-κB/AP-1 pathway in a Dectin-1-dependent manner, similar to natural β-glucans. The lead PAS significantly polarizes primary human macrophages towards M1 phenotype compared to other β-glucans such as lentinan, laminarin, and curdlan.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Activation of macrophages by linear (1right-arrow3)-beta-D-glucans. Impliations for the recognition of fungi by innate immunity.J Biol Chem. 2002 Sep 27;277(39):36825-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206756200. Epub 2002 Jul 24. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12140296
-
Curdlan (Alcaligenes faecalis) (1→3)-β-d-Glucan Oligosaccharides Drive M1 Phenotype Polarization in Murine Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages via Activation of MAPKs and NF-κB Pathways.Molecules. 2019 Nov 22;24(23):4251. doi: 10.3390/molecules24234251. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31766621 Free PMC article.
-
A (1→6)-Branched (1→4)-β-d-Glucan from Grifola frondosa Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cytokine Production in RAW264.7 Macrophages by Binding to TLR2 Rather than Dectin-1 or CR3 Receptors.J Nat Prod. 2020 Feb 28;83(2):231-242. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b00584. Epub 2020 Jan 22. J Nat Prod. 2020. PMID: 31967822
-
Medicinal importance of fungal beta-(1-->3), (1-->6)-glucans.Mycol Res. 2007 Jun;111(Pt 6):635-52. doi: 10.1016/j.mycres.2007.02.011. Epub 2007 Mar 7. Mycol Res. 2007. PMID: 17590323 Review.
-
β-(1→3),(1→6)-Glucans: medicinal activities, characterization, biosynthesis and new horizons.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Oct;99(19):7893-906. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6849-x. Epub 2015 Aug 8. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26252967 Review.
Cited by
-
Lentinan progress in inflammatory diseases and tumor diseases.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jan 3;29(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01585-7. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38172925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic targeting of obesity-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 17;15:1456948. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1456948. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39897964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How do tumours outside the gastrointestinal tract respond to dietary fibre supplementation?BMJ Oncol. 2023 Nov 10;2(1):e000107. doi: 10.1136/bmjonc-2023-000107. eCollection 2023. BMJ Oncol. 2023. PMID: 39886510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglia-Dependent Reversal of Depression-Like Behaviors in Chronically Stressed Mice by Administration of a Specific Immuno-stimulant β-Glucan.Neurochem Res. 2024 Feb;49(2):519-531. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04056-x. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 37962706
-
Branched Polymer Architecture for Modulating Interactions in Material-Bio Interface.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2025 Jun;22(4):481-504. doi: 10.1007/s13770-024-00699-1. Epub 2025 Mar 8. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2025. PMID: 40056364 Review.
References
-
- Wijesekara I, Pangestuti R, Kim SK. Biological activities and potential health benefits of sulfated polysaccharides derived from marine algae. Carbohyd Polym. 2011;84:14–21. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.10.062. - DOI
-
- Bohn, J. A. & BeMiller, J. N. 1->3)-beta-D-glucans as biological response modifiers: a review of structure-functional activity relationships. Carbohyd Polym28, 3–14 (1995).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

