Digit ratio (2D:4D) and maternal testosterone-to-estradiol ratio measured in early pregnancy
- PMID: 35945232
- PMCID: PMC9363442
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-17247-3
Digit ratio (2D:4D) and maternal testosterone-to-estradiol ratio measured in early pregnancy
Abstract
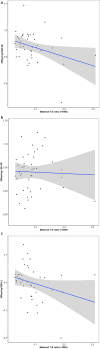
The ratio of index to ring finger (2D:4D) has been hypothesised to indicate prenatal androgen exposure, yet evidence for its validity is lacking. We report the first pre-registered study to investigate mothers' early pregnancy sex hormone concentrations in relation to their children's digit ratios measured at 18-22-month follow-up. Although the testosterone (T) to estradiol (E) ratio correlated negatively with right hand digit ratio (R2D:4D) and directional asymmetry (right-minus-left) in digit ratio (D[R-L]), neither effect remained statistically significant once demographic and obstetric covariates were controlled for. Nevertheless, the multivariate level of analysis did reveal that T correlated positively with left hand digit ratio (L2D:4D) and negatively with D[R-L]. However, the first of these effects is in the opposite direction to that predicted by theory. Taken together, the results of our study suggest research with larger samples is required to determine whether digit ratios are valid proxies for maternal sex hormone exposure.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources