Generation of bioluminescent enzyme immunoassay for ferritin by single-chain variable fragment and its NanoLuc luciferase fusion
- PMID: 35945290
- PMCID: PMC9531656
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-022-04261-7
Generation of bioluminescent enzyme immunoassay for ferritin by single-chain variable fragment and its NanoLuc luciferase fusion
Abstract
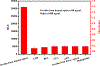
Ferritin, widely present in liver and spleen tissue, is considered as a serological biomarker for liver diseases and cancers. The detection of ferritin may be an important tool in health diagnosis. In this study, 14 non-immunized chicken spleens were utilized to construct a single-chain fragment (scFv) phage library. After 4 rounds of panning, 7 unique clones were obtained. The optimal clone was further screened and combined with NanoLuc luciferase (Nluc) as a dual functional immunoprobe to bioluminescent enzyme immunoassay (BLEIA), which was twice as sensitive as its parental scFv-based double-sandwich enzyme-linked immunoassay (ds-ELISA). The cross-reactivity analysis revealed that the proposed methods were highly selective and suitable for clinical detection. To further verify the performance of the immunoassays, serum samples were tested by the proposed methods and a commercial ELISA kit, and there was a good correlation between the results. These results suggested that scFv fused with Nluc might be a powerful dual functional tool for rapid, practically reliable, and highly sensitive ferritin detection.
Keywords: Bioluminescent enzyme immunoassay; Biomarker; Ferritin; NanoLuc luciferase; Single-chain variable fragment.
© 2022. Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests to publish this paper.
Figures

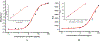

References
-
- Pauline M Harrison PA (1996) The ferritins” molecular properties, iron storage function and cellular regulation Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1275:161–203 - PubMed
-
- Vohra I, Attar B, Katiyar V, Palacios P, Randhawa T, Baig MA, Flores E, Wang Y, Mutneja H, Sharma S, Lingamneni P, Farooq MZ, Bhaskaran N, Gandhi S, Vettiankal G, Demetria M (2021) Evaluation of Ferritin and Transferrin Ratio as a Prognostic Marker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J Gastrointest Cancer 52 (1):201–206. doi: 10.1007/s12029-020-00373-4 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 201903010034/Guangzhou Science and Technology Foundation
- 2018A030313926/Natural Resources Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2019B020209009/Science and Technology Foundation Key R&D Program of Guangdong Province
- R35 ES030443/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES004699/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States

