Whole genome non-invasive prenatal testing in prenatal screening algorithm: clinical experience from 12,700 pregnancies
- PMID: 35945516
- PMCID: PMC9364619
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-022-04966-8
Whole genome non-invasive prenatal testing in prenatal screening algorithm: clinical experience from 12,700 pregnancies
Abstract
Background: A fast adoption of a non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) in clinical practice is a global tendency last years. Firstly, in Russia according a new regulation it was possible to perform a widescale testing of pregnant women in chromosomal abnormality risk. The aim of the study-to assess efficiency of using NIPT as a second-line first trimester screening test in Moscow.
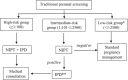
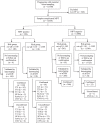
Methods: Based on the first trimester combined prenatal screening results 12,700 pregnant women were classified as a high-risk (cut-off ≥ 1:100) and an intermediate-risk (cut-off 1:101 - 1:2500) groups followed by whole genome NIPT. Women from high-risk group and those who had positive NIPT results from intermediate-risk group were considered for invasive prenatal diagnostic.
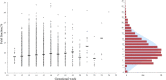
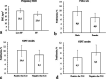
Results: 258 (2.0%) samples with positive NIPT results were detected including 126 cases of trisomy 21 (T21), 40 cases of T18, 12 cases of T13, 41 cases of sex chromosome aneuploidies (SCAs) and 39 cases of rare autosomal aneuploidies (RAAs) and significant copy number variations (CNVs). Statistically significant associations (p < 0.05) were revealed for fetal fraction (FF) and both for some patient's (body mass index and weight) and fetus's (sex and high risk of aneuploidies) characteristics. NIPT showed as a high sensitivity as specificity for common trisomies and SCAs with an overall false positive rate 0.3%.
Conclusions: NIPT demonstrated high sensitivity and specificity. As a second-line screening test it has shown a high efficiency in detecting fetus chromosomal anomalies as well as it could potentially lower the number of invasive procedures in pregnant women.
Keywords: Amniocentesis; Fetal aneuploidy; NIPT; Non-invasive prenatal testing; Prenatal screening; Rare autosomal trisomies; Trisomy 13; Trisomy 18; Trisomy 21; cfDNA.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Baranov AA, Namazova-Baranova LS, Albitskiy V, Terletskaya RN. Tendencies of infantile and child mortality in the conditions of implementation of the modern strategy of development of health care of the Russian Federation. Vestnic RAMN. 2017;72(5):375–382.
-
- Sukhikh GT, Karetnikova NA, Baranova EE, Shubina ES, Korostin DO, Evdokimov AN, et al. Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of aneuploidies by high-throughput sequencing (NGS) in a group of high-risk women. Obstet Gynecol (Moscow) 2016;6:129–157.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

