Polyethylene glycol recombinant human growth hormone in Chinese prepubertal slow-growing short children: doses reported in a multicenter real-world study
- PMID: 35945517
- PMCID: PMC9364582
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-022-01101-8
Polyethylene glycol recombinant human growth hormone in Chinese prepubertal slow-growing short children: doses reported in a multicenter real-world study
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the effectiveness of individualized-dose polyethylene glycol recombinant human growth hormone (PEG-rhGH) for short stature.
Methods: This real-world study enrolled children with short stature in 19 hospitals throughout China. They were treated with PEG-rhGH for 6 months. The starting dosage ranged from 0.10 to 0.20 mg/kg/week. The primary outcome was the change in height standard deviation score (ΔHt SDS).
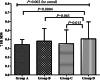
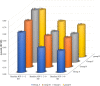
Results: Five hundred and ten patients were included and grouped based on dosage as A (0.10-0.14 mg/kg/week), B (0.15-0.16 mg/kg/week), C (0.17-0.19 mg/kg/week), and D (0.20 mg/kg/week). The mean 6-month ΔHt SDS for the total cohort was 0.49 ± 0.27, and the means differed among the four dose groups (P = 0.002). The ΔHt SDS was lower in group A than in groups B (LSM difference [95%CI], -0.09 [-0.17, -0.01]), C (LSM difference [95%CI], -0.10 [-0.18, -0.02]), and D (LSM difference [95%CI], -0.13 [-0.21, -0.05]) after adjusting baseline covariates. There were no significant differences among groups B, C, and D. When the baseline IGF-1 was < -2 SDS or > 0 SDS, the △Ht SDS was not different among the four groups (P = 0.931 and P = 0.400). In children with baseline IGF-1 SDS of -2 ~ 0 SDS, a higher dosage was associated with a better treatment effect (P = 0.003), and the △Ht SDS was lower in older children than in younger ones (P < 0.001).
Conclusions: PEG-rhGH could effectively increase height in prepubertal short children. When the baseline IGF-1 was < -2 SDS, 0.10 mg/kg/week could be a starting dose. In other IGF-1 statuses, 0.15-0.20 mg/kg/week might be preferred.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT03249480 , retrospectively registered.
Keywords: Children; Multicenter; Polyethylene glycol recombinant human growth hormone; Real-world study; Short stature.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Barstow C, Rerucha C. Evaluation of Short and Tall Stature in Children. Am Fam Physician. 2015;92(1):43–50. - PubMed
-
- Wit JM: ICPED. International Classification of Pediatric Endocrine Diagnoses. Short stature. http://www.icped.org/revisions/0/2015/diagnoses/#!/1. Accessed May 25, 2021; 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 2017ZX09304029-001-002/National Science and Technology Major Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous