Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Brief Emotion and Regulation Beliefs Scale in Chinese nursing students
- PMID: 35945531
- PMCID: PMC9364589
- DOI: 10.1186/s12912-022-00992-1
Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Brief Emotion and Regulation Beliefs Scale in Chinese nursing students
Abstract
Background: Nursing students are experiencing complex learning environments and will experience complex work environments in future clinical work, which lead to emotional problems easily. However, one's beliefs about controlling their emotions portend a series of vital psychological outcomes. So, it is especially important to search for suitable tools to assess the emotion and regulation beliefs of nursing students and give timely intervention to improve their physical and mental health. This study aimed to translate the American version of the Emotion and Regulation Beliefs Scale (ERBS) into Chinese, revise the original scale and form a simplified version, and assess the reliability and validity of the brief Chinese version in nursing students.
Methods: The study adopted a cross-sectional design and the multistage sampling design. The ERBS was translated into Chinese, and the reliability and validity of the Chinese version were tested in 980 nursing students.
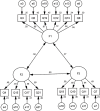
Results: The content validity index was 0.920. Exploratory factor analysis supported a three-factor model for the Chinese version of Brief-ERBS, and confirmatory factor analysis indicated that the model fit the Brief-ERBS well. Furthermore, the three-factors model was obtained by using exploratory factor analysis, explaining 51.023% variance, and the communalities of the items ranged from 0.359 to 0.680. With modified confirmatory factor analysis, the fit indices were chi-square/degree of freedom (CMIN/DF) = 4.092, goodness of fit index (GFI) = 0.949, adjusted goodness of fit index (AGFI) = 0.927, comparative fit index (CFI) = 0.913, incremental fit index (IFI) = 0.914, Tucker Lewis index (TLI) = 0.908, root-mean-square error of approximation (RMSEA) = 0.061. The two-tailed independent samples t-test showed the scores of the top (50%) and low (50%) groups reached the level of significance (P < 0.001). A highly positive correlation between the Brief-ERBS total score and the ERBS total score was found (r = 0.972, P < 0.01). The Cronbach's α coefficient of the scale was 0.798, the split-half reliability coefficient was 0.784, and the retest coefficient was 0.879.
Conclusion: The Chinese version of Brief-ERBS has good reliability and validity, and may be used for the beliefs about emotional management in Chinese nursing students.
Keywords: Emotions; Nursing; Reliability; Students; Validity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the self-directed learning instrument in Chinese nursing students.BMC Nurs. 2023 Feb 24;22(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12912-023-01201-3. BMC Nurs. 2023. PMID: 36823629 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the mental vulnerability questionnaire for the undergraduate students.Perspect Psychiatr Care. 2020 Apr;56(2):409-414. doi: 10.1111/ppc.12449. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Perspect Psychiatr Care. 2020. PMID: 31691293
-
Evaluation of reliability and validity regarding the Chinese version of Critical Cultural Competence Scale for clinical nurses.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Oct 28;47(10):1425-1434. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.210695. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 36411694 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese, English.
-
Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Self-Efficacy Perception Scale for Administrator Nurses.Int J Nurs Sci. 2023 Sep 28;10(4):503-510. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnss.2023.09.015. eCollection 2023 Oct. Int J Nurs Sci. 2023. PMID: 38020844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and psychometric testing of Perceived Preoperative Nursing Care Competence Scale for Nursing Students (PPreCC-NS).Nurse Educ Today. 2023 Jan;120:105632. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2022.105632. Epub 2022 Nov 11. Nurse Educ Today. 2023. PMID: 36410082 Review.
Cited by
-
Validation of the Chinese version of the Oslo-3 Social Support Scale among nursing students: a study based on Classical Test Theory and Item Response Theory models.BMC Nurs. 2024 May 30;23(1):360. doi: 10.1186/s12912-024-02033-5. BMC Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38816705 Free PMC article.
-
The reliability and validity of the depression change expectancy scale in college students: a cross-sectional study in China.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 10;15(1):8198. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92573-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40065082 Free PMC article.
-
Translation and validation of the Chinese version of the Attitudes Related to Trauma-Informed Care (ARTIC-C) scale in nursing inters: a psychometric analysis.BMC Nurs. 2024 Dec 18;23(1):915. doi: 10.1186/s12912-024-02612-6. BMC Nurs. 2024. PMID: 39696371 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the Chinese version of academic goals orientation questionnaire in nursing student: a study based on SEM and IRT multidimensional models.BMC Nurs. 2023 Dec 6;22(1):465. doi: 10.1186/s12912-023-01630-0. BMC Nurs. 2023. PMID: 38057897 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the personal characteristics of decent work perception for nursing students in China using latent profile analysis.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Mar 20;24(1):315. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05206-7. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 38509488 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreescu C, Sheu LK, Tudorascu D, Gross JJ, Walker S, Banihashemi L, et al. Emotion reactivity and regulation in late-life generalized anxiety disorder: functional connectivity at baseline and post-treatment. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2015;23(2):200–214. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2014.05.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

