Comparison of ONT and CCS sequencing technologies on the polyploid genome of a medicinal plant showed that high error rate of ONT reads are not suitable for self-correction
- PMID: 35945546
- PMCID: PMC9364492
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-022-00644-1
Comparison of ONT and CCS sequencing technologies on the polyploid genome of a medicinal plant showed that high error rate of ONT reads are not suitable for self-correction
Abstract
Background: Many medicinal plants are known for their complex genomes with high ploidy, heterozygosity, and repetitive content which pose severe challenges for genome sequencing of those species. Long reads from Oxford nanopore sequencing technology (ONT) or Pacific Biosciences Single Molecule, Real-Time (SMRT) sequencing offer great advantages in de novo genome assembly, especially for complex genomes with high heterozygosity and repetitive content. Currently, multiple allotetraploid species have sequenced their genomes by long-read sequencing. However, we found that a considerable proportion of these genomes (7.9% on average, maximum 23.7%) could not be covered by NGS (Next Generation Sequencing) reads (uncovered region by NGS reads, UCR) suggesting the questionable and low-quality of those area or genomic areas that can't be sequenced by NGS due to sequencing bias. The underlying causes of those UCR in the genome assembly and solutions to this problem have never been studied.
Methods: In the study, we sequenced the tetraploid genome of Veratrum dahuricum (Turcz.) O. Loes (VDL), a Chinese medicinal plant, with ONT platform and assembled the genome with three strategies in parallel. We compared the qualities, coverage, and heterozygosity of the three ONT assemblies with another released assembly of the same individual using reads from PacBio circular consensus sequencing (CCS) technology, to explore the cause of the UCR.
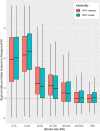
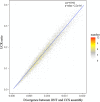
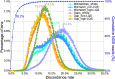
Results: By mapping the NGS reads against the three ONT assemblies and the CCS assembly, we found that the coverage of those ONT assemblies by NGS reads ranged from 49.15 to 76.31%, much smaller than that of the CCS assembly (99.53%). And alignment between ONT assemblies and CCS assembly showed that most UCR can be aligned with CCS assembly. So, we conclude that the UCRs in ONT assembly are low-quality sequences with a high error rate that can't be aligned with short reads, rather than genomic regions that can't be sequenced by NGS. Further comparison among the intermediate versions of ONT assemblies showed that the most probable origin of those errors is a combination of artificial errors introduced by "self-correction" and initial sequencing error in long reads. We also found that polishing the ONT assembly with CCS reads can correct those errors efficiently.
Conclusions: Through analyzing genome features and reads alignment, we have found the causes for the high proportion of UCR in ONT assembly of VDL are sequencing errors and additional errors introduced by self-correction. The high error rates of ONT-raw reads make them not suitable for self-correction prior to allotetraploid genome assembly, as the self-correction will introduce artificial errors to > 5% of the UCR sequences. We suggest high-precision CCS reads be used to polish the assembly to correct those errors effectively for polyploid genomes.
Keywords: Allotetraploid; Homozygous variants; Low-quality sequences; ONT-based assembly; Veratrum dahuricum.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comparison of the two up-to-date sequencing technologies for genome assembly: HiFi reads of Pacific Biosciences Sequel II system and ultralong reads of Oxford Nanopore.Gigascience. 2020 Dec 15;9(12):giaa123. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giaa123. Gigascience. 2020. PMID: 33319909 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating long-read de novo assembly tools for eukaryotic genomes: insights and considerations.Gigascience. 2022 Dec 28;12:giad100. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giad100. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Gigascience. 2022. PMID: 38000912 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of De Novo Assembly Strategies for Bacterial Genomes.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 17;22(14):7668. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147668. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299288 Free PMC article.
-
Oxford Nanopore MinION Sequencing and Genome Assembly.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016 Oct;14(5):265-279. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2016.05.004. Epub 2016 Sep 17. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27646134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant genome sequence assembly in the era of long reads: Progress, challenges and future directions.Quant Plant Biol. 2022 Mar 11;3:e5. doi: 10.1017/qpb.2021.18. eCollection 2022. Quant Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 37077982 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Application of third-generation sequencing to herbal genomics.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Mar 7;14:1124536. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1124536. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36959935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of third-generation sequencing technology in the genetic testing of thalassemia.Mol Cytogenet. 2024 Dec 18;17(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s13039-024-00701-4. Mol Cytogenet. 2024. PMID: 39696632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA isoform expression landscape of the human dorsal root ganglion generated from long-read sequencing.Pain. 2024 Nov 1;165(11):2468-2481. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003255. Epub 2024 May 16. Pain. 2024. PMID: 38809314
-
RNA isoform expression landscape of the human dorsal root ganglion (DRG) generated from long read sequencing.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 1:2023.10.28.564535. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.28.564535. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Pain. 2024 Nov 1;165(11):2468-2481. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003255. PMID: 37961262 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Grants and funding
- 031/2017/A1/The Science and Technology Development Fund Macau SAR
- 3102019JC007/the Talents Team Construction Fund of Northwestern Polytechnical University (NWPU), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- 5113190037/Ten Thousand Talent Plans for Young Top-notch Talents of Yunnan Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

