Cytoreductive prostatectomy improves survival outcomes in patients with oligometastases: a systematic meta-analysis
- PMID: 35945562
- PMCID: PMC9361652
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-022-02715-x
Cytoreductive prostatectomy improves survival outcomes in patients with oligometastases: a systematic meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Whether cytoreductive prostatectomy (CRP) should be performed in patients with oligometastatic prostate cancer (OPC) remains controversial. The goal of this systematic meta-analysis was to assess the efficacy of CRP as a treatment for OPC.
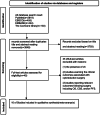
Methods: This systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis statement. Data sources included publications in the PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, EBSCO, and Web of Science (SCI) databases as of May 2022. Eligible articles included prospective studies comparing the efficacy of CRP to a lack of CRP in patients with OPC.
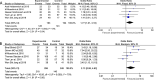
Results: In total, 10 publications incorporating 888 patients were analyzed. Tumor-reducing prostatectomy was found to have no significant effect on long-term or short-term OS [OR = 2.26, 95% CI (0.97, 5.28), P = 0.06] and [OR = 1.73, 95% CI (0.83, 3.58), P = 0.14], but it significantly improved patient long-term or short-term CSS [OR = 1.77, 95% CI (1.01, 310), P = 0.04] and [OR = 2.71, 95% CI (1.72, 4.29), P < 0.0001] and PFS [OR = 1.93, 95% CI (1.25, 2.97), P = 0.003].
Conclusion: These results suggest that cytoreductive prostatectomy can confer survival benefits to OPC patients.
Trial registration: INPLASY protocol 202260017 https://doi.org/10.37766/inplasy2022.6.0017 .
Keywords: Cancer-specific survival; Cytoreductive prostatectomy; Oligometastases; Overall survival; Progression-free survival.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cytoreductive prostatectomy may improve oncological outcomes in patients with oligometastatic prostate cancer: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis.Investig Clin Urol. 2023 May;64(3):242-254. doi: 10.4111/icu.20230058. Investig Clin Urol. 2023. PMID: 37341004 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoreductive radical prostatectomy versus systemic therapy and radiation therapy in metastatic prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Urologia. 2022 Feb;89(1):16-30. doi: 10.1177/03915603211036631. Epub 2021 Aug 6. Urologia. 2022. PMID: 34355602
-
Evaluating the effectiveness of cytoreductive surgery in oligometastatic prostate cancer: insights from quantitative analysis and retrospective cohort studies.Int J Surg. 2025 Jan 1;111(1):122-134. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001968. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 39007913 Free PMC article.
-
Local treatment benefits patients with oligometastatic prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Urol. 2024 Nov;31(11):1223-1233. doi: 10.1111/iju.15540. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Int J Urol. 2024. PMID: 39011667
-
The cytoreductive prostatectomy in metastatic prostate cancer: what the individual trials are hoping to answer.BJU Int. 2020 Jun;125(6):792-800. doi: 10.1111/bju.15055. Epub 2020 Apr 7. BJU Int. 2020. PMID: 32176456 Review.
Cited by
-
Current Controversy and Developments Regarding the Cytoreductive Prostatectomy for Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Jan-Dec;22:15330338231216011. doi: 10.1177/15330338231216011. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 38105493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytoreductive prostatectomy may improve oncological outcomes in patients with oligometastatic prostate cancer: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis.Investig Clin Urol. 2023 May;64(3):242-254. doi: 10.4111/icu.20230058. Investig Clin Urol. 2023. PMID: 37341004 Free PMC article.
-
An Updated Systematic and Comprehensive Review of Cytoreductive Prostatectomy for Metastatic Prostate Cancer.Curr Oncol. 2023 Feb 10;30(2):2194-2216. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30020170. Curr Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36826131 Free PMC article.
-
Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer-The Middle Child Syndrome.J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 21;12(23):7198. doi: 10.3390/jcm12237198. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38068251 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Crocetto F, Buonerba C, Caputo V, Ferro M, Persico F, Trama F, Iliano E, Rapisarda S, Bada M, Facchini G, Verde A, Placido S, Barone B. Urologic malignancies: advances in the analysis and interpretation of clinical findings. Future Sci OA. 2021;7(4):FSO674. doi: 10.2144/fsoa-2020-0210. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

