Salvia-Nelumbinis naturalis improves lipid metabolism of NAFLD by regulating the SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway
- PMID: 35945571
- PMCID: PMC9361555
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-022-03697-9
Salvia-Nelumbinis naturalis improves lipid metabolism of NAFLD by regulating the SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Salvia-Nelumbinis naturalis (SNN), the extract of Chinese herbal medicine, has shown effects on NAFLD. This study aims to explore the underlying mechanism of SNN for regulating the lipid metabolism disorder in NAFLD based on the SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway.
Methods: Male C57BL/6J mice fed with a high-fat diet (HFD) were used to establish the NAFLD model. Dynamic changes of mice including body weight, liver weight, serological biochemical indexes, liver histopathological changes, and protein level of AMPK and SIRT1 were monitored. After18 weeks, SNN treatment was administrated to the NAFLD mice for another 4 weeks. Besides the aforementioned indices, TC and TG of liver tissues were also measured. Western blot and quantitative RT-PCR were used to detect the expression and/or activation of SIRT1 and AMPK, as well as the molecules associated with lipid synthesis and β-oxidation. Furthermore, AML12 cells with lipid accumulation induced by fatty acids were treated with LZG and EX527 (SIRT1 inhibitor) or Compound C (AMPK inhibitor ) to confirm the potential pharmacological mechanism.
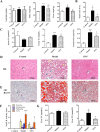
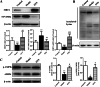
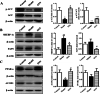
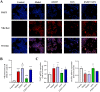
Results: Dynamic observation found the mice induced by HFD with gradually increased body and liver weight, elevated serum cholesterol, hepatic lipid accumulation, and liver injury. After 16 weeks, these indicators have shown obvious changes. Additionally, the hepatic level of SIRT1 and AMPK activation was identified gradually decreased with NAFLD progress. The mice with SNN administration had lower body weight, liver weight, and serum level of LDL-c and ALT than those of the NAFLD model. Hepatosteatosis and hepatic TG content in the liver tissues of the SNN group were significantly reduced. When compared with control mice, the NAFLD mice had significantly decreased hepatic expression of SIRT1, p-AMPK, p-ACC, ACOX1, and increased total Acetylated-lysine, SUV39H2, and SREBP-1c. The administration of SNN reversed the expression of these molecules. In vitro experiments showed the effect of SNN in ameliorating hepatosteatosis and regulating the expression of lipid metabolism-related genes in AML12 cells, which were diminished by EX527 or Compound C co-incubation.
Conclusions: Taken together, the SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway, involved in hepatic lipid synthesis and degradation, plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of NAFLD development. The regulation of SIRT1/AMPK signaling greatly contributes to the underlying therapeutic mechanism of SNN for NAFLD.
Keywords: AMPK; Lipid metabolism; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; SIRT1; Salvia-Nelumbinis naturalis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protopanaxadiol ameliorates NAFLD by regulating hepatocyte lipid metabolism through AMPK/SIRT1 signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Apr;160:114319. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114319. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36724639
-
LB100 ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via the AMPK/Sirt1 pathway.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Dec 7;25(45):6607-6618. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i45.6607. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31832001 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrahydropalmatine ameliorates hepatic steatosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by switching lipid metabolism via AMPK-SREBP-1c-Sirt1 signaling axis.Phytomedicine. 2023 Oct;119:155005. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155005. Epub 2023 Aug 5. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37562090
-
Natural compounds against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A review on the involvement of the LKB1/AMPK signaling pathway.Phytother Res. 2023 Dec;37(12):5769-5786. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8020. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Phytother Res. 2023. PMID: 37748097 Review.
-
The AMPK pathway in fatty liver disease.Front Physiol. 2022 Aug 25;13:970292. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.970292. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36203933 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CircLDLR acts as a sponge for miR-667-5p to regulate SIRT1 expression in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Lipids Health Dis. 2022 Nov 29;21(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s12944-022-01740-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2022. PMID: 36443854 Free PMC article.
-
Ginkgolide B attenuates hyperlipidemia by restoring sphingolipid homeostasis and activating PPARα and Nrf2 pathways.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 6;15(1):28774. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14626-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40770408 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC6 inhibitor ACY-1215 protects from nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via inhibiting CD14/TLR4/MyD88/MAPK/NFκB signal pathway.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 27;10(13):e33740. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33740. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39055804 Free PMC article.
-
Jiangzhi Granule Ameliorates JNK-Mediated Mitochondrial Dysfunction to Reduce Lipotoxic Liver Injury in NASH.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025 Jan 6;18:23-36. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S492174. eCollection 2025. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025. PMID: 39802620 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuin 1 Inhibits Fatty Acid Synthesis through Forkhead Box Protein O1-Mediated Adipose Triglyceride Lipase Expression in Goat Mammary Epithelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 14;25(18):9923. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189923. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kanwal F, Shubrook JH, Younossi Z, Natarajan Y, Bugianesi E, Rinella ME, Harrison SA, Mantzoros C, Pfotenhauer K, Klein S, et al. Preparing for the NASH Epidemic: A Call to Action. Gastroenterology. 2021;161(3):1030–1042 e1038. - PubMed
-
- Neuschwander-Tetri BA. Therapeutic Landscape for NAFLD in 2020. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(7):1984–1998 e1983. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

