Role of m6A writers, erasers and readers in cancer
- PMID: 35945641
- PMCID: PMC9361621
- DOI: 10.1186/s40164-022-00298-7
Role of m6A writers, erasers and readers in cancer
Abstract
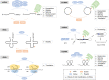
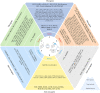
The N(6)-methyladenosine (m6A) modification is the most pervasive modification of human RNAs. In recent years, an increasing number of studies have suggested that m6A likely plays important roles in cancers. Many studies have demonstrated that m6A is involved in the biological functions of cancer cells, such as proliferation, invasion, metastasis, and drug resistance. In addition, m6A is closely related to the prognosis of cancer patients. In this review, we highlight recent advances in understanding the function of m6A in various cancers. We emphasize the importance of m6A to cancer progression and look forward to describe future research directions.
Keywords: Cancer; Erasers; N6-methyladenosine (m6A); Readers; Writers.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

