Which combination of different ultrasonography modalities is more appropriate to diagnose breast cancer?: A network meta-analysis (a PRISMA-compliant article)
- PMID: 35945707
- PMCID: PMC9351919
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029955
Which combination of different ultrasonography modalities is more appropriate to diagnose breast cancer?: A network meta-analysis (a PRISMA-compliant article)
Abstract
Background: Abundant amount of literature that analyze the various detection of different ultrasound methods, no comprehensive literature that investigates the diagnostic values of breast cancer (BC) by different ultrasonography modalities through a network meta-analysis (NMA) has been made available. Each imaging diagnostic examination has its own advantages and disadvantages, and any imaging examination is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis of the disease. Thus, this study aimed to compare diagnostic values among different ultrasonography modalities, including the information of 2-dimension, stiffness and blood flow, by a network meta-analysis in the hopes of understanding which imaging methods are better and which combination of different ultrasonography modalities is more appropriate to diagnose BC.
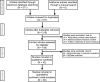
Methods: We made use of Cochrane Library, PubMed, and Embase in order to obtain literature and papers. The combination analysis of both direct and indirect evidence in terms of sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value(NPV) and accuracy was conducted so as to assess the odds ratios (ORs) and surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) values of the 8 different ultrasound methods.
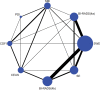
Results: A total of 36 eligible diagnostic tests regarding 8 ultrasound methods were included in the study. According to this network meta-analysis, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) 4b exhibited higher specificity, PPV, and accuracy and lower sensitivity and NPV than BI-RADS 4a. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) had the highest sensitivity, PPV, NPV and accuracy and superb microvascular imaging (SMI) had the highest specificity among color Doppler flow imaging (CDFI), power Doppler imaging(PDI), SMI and CEUS. There was no significant difference in diagnostic indexes between SMI and CEUS. Shear wave elastrography (SWE) had higher PPV and accuracy and lower sensitivity, specificity NPV than strain elastography (SE).
Conclusion: The results of this network meta-analysis suggested more appropriate combination of different ultrasound modalities is BI-RADS 4b, SMI, and SWE for the diagnosis of breast cancer.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The application of multimodal ultrasound examination in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast lesions of BI-RADS category 4.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 9;12:1596100. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1596100. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40552183 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Free-hand ultrasound strain elastography in evaluation of soft tissue tumors.J Ultrasound. 2024 Sep;27(3):589-598. doi: 10.1007/s40477-024-00893-w. Epub 2024 Jul 25. J Ultrasound. 2024. PMID: 39052198
Cited by
-
Using a combination of superb microvascular imaging and other auxiliary ultrasound techniques to increase the accuracy of gray-scale ultrasound for breast masses.BMC Cancer. 2024 Feb 16;24(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-11981-9. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38365653 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic value of real-time ultrasound elastography and contrast-enhanced ultrasound in BI-RADS 4A breast lesions.Gland Surg. 2025 Mar 31;14(3):488-497. doi: 10.21037/gs-2025-93. Epub 2025 Mar 26. Gland Surg. 2025. PMID: 40256483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afifi AM, Saad AM, Al-Husseini MJ, et al. . Causes of death after breast cancer diagnosis: a US population-based analysis. Cancer. 2020;126:1559–67. - PubMed
-
- Youlden DR, Baade PD, Walker R, et al. . Breast cancer incidence and survival among young females in Queensland, Australia. J Adolesc Young Adult Oncol. 2020;9:402–9. - PubMed
-
- Rao AA, Feneis J, Lalonde C, et al. . A pictorial review of changes in the BI-RADS fifth edition. Radiographics. 2016;36:623–39. - PubMed
-
- Zhong L, Wang C. Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound superb microvascular imaging for breast tumor: a meta-analysis. Med Ultrason. 2020;22:313–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

