Von Willebrand factor (vWF) in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF): A retrospective observational study
- PMID: 35945712
- PMCID: PMC9351886
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029854
Von Willebrand factor (vWF) in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF): A retrospective observational study
Abstract
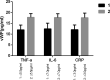
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is associated with endothelial damage and inflammation. In addition, von Willebrand factor (vWF) has been discovered as a biomarker of endothelial dysfunction. Therefore, the study aims to investigate the association between vWF level and HFpEF. Moreover, we analyzed a potential correlation between vWF and inflammatory factors, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and interleukin (IL)-6. We recruited altogether 272 hospitalized patients from The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, 88 of whom were HFpEF patients, 88 were non-heart failure patients, and 96 were healthy controls from the medical examination center of the hospital. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and double antibody sandwich immunochromatography were used for testing vWF, tissue plasminogen activator, galectin-3, nitric oxide, TNF-α, IL-6, and CRP. The HFpEF group's levels of vWF, IL-6, TNF-α, CRP, tissue plasminogen activator, galectin-3, and nitric oxide were statistically higher than those of non-heart failure and healthy control ones (F = 403.563, 21.825, 20.678, 39.609, 35.411, 86.407, 74.605; all P = .000). the highest level of vWF was observed in class IV (New York Heart Association) of HFpEF patients and the significant difference is <.05 (P < .001). An increasing level of vWF were shown in groups (CRP: CRP >3 mg/L group and CRP ≤3 mg/L group; IL-6: IL-6 <7.0 pg/mL group and IL-6 ≥7.0 pg/mL group; TNF-α: TNF-α <5.5 pg/mL group and TNF-α ≥5.5 pg/mL group) with higher level of IL-6, TNF-α, CRP. A multiple regression analysis regarding the relationship of vWF and inflammation markers was performed among the HFpEF patients. Further, statistical significance of the analysis remained after adjusting variables such as body mass index, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, total cholesterol, coronary artery disease, and type 2 diabetes mellitus (β = 0.406, t = 4.579, P < .001; β = 0.323, t = 3.218, P < .001; β = 0.581, t = 6.922, P < .001). Our study shows that elevated vWF levels are associated with HFpEF, and it may serve as a potential biomarker for HFpEF severity. We also found that increased vWF levels are positively correlated to IL-6, TNF-α, and CRP, which may provide a clue for further researching the pathogenesis of HFpEF.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
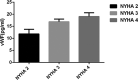
References
-
- Seferovic PM, Ponikowski P, Anker SD, et al. . Clinical practice update on heart failure 2019: pharmacotherapy, procedures, devices and patient management. an expert consensus meeting report of the heart failure association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail. 2019;21:1169–1186. - PubMed
-
- van der Meer P, Gaggin HK, Dec GW. ACC/AHA versus ESC guidelines on heart failure: JACC Guideline Comparison. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73:2756–2768. - PubMed
-
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. . 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA focused update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70:776–803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

