A systematic review of the efficacy of donepezil hydrochloride combined with nimodipine on treating vascular dementia
- PMID: 35945739
- PMCID: PMC9351939
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029307
A systematic review of the efficacy of donepezil hydrochloride combined with nimodipine on treating vascular dementia
Abstract
Background: Vascular dementia (VaD) is a comprehensive syndrome related to the damage of cognitive function and various cerebral vascular illnesses. VaD is also generally recognized as the second most common type of dementia after Alzheimer disease, contributing to 30% of the dementia population in Asia and developing countries. The ability of donepezil hydrochloride and nimodipine had been respectively proven in improving cognitive function in vascular dementia. However, whether the combined application of both drugs contribute to better efficacy remains as a research hotspot. Studies had shown definite satisfactory result with such combination, however evidence-based evaluation of the efficacy is still lacking. Therefore, meta-analysis is employed in this study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of using donepezil hydrochloride combined with nimodipine in treating VaD to provide references for clinical treatments. The efficacy of donepezil hydrochloride combined with nimodipine on treating vascular dementia is systematically reviewed to provide evidence-based references for clinical applications.
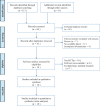
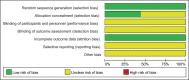
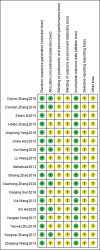
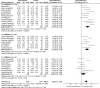
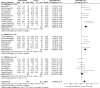
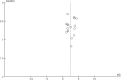
Methods: Both Chinese and English databases were searched from the start till August, 2020 for any RCT regarding the combined use of the 2 drugs in treating vascular dementia. Two investigators would later evaluate and screened out research and data based on an improved Jaded scale. Software Rev Man 5.3.0 was employed to carry out meta-analysis on clinical effificacy, mini-mental state examination (MMSE) ratings, activity of daily living (ADL) ratings, and clinical dementia scale (CDR) ratings.
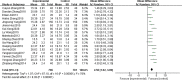
Results: Donepezil hydrochloride combined with nimodipine had demonstrated satisfactory efficacy on the treatment of vascular dementia. Improvements were namely spotted on MMSE scale, ADL scale, and CDR scale, with the utmost efficacy by 12 weeks after intervention.
Conclusions: Donepezil hydrochloride combined with nimodipine had good efficacy in the treatment of patients with vascular dementia, mainly in terms of improving the Simple MMSE scores, the ability to use daily living scale (ADL) scores and the CDR, and the best results were obtained after 12 weeks of intervention. Such conclusion should be cautiously evaluated.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of ginkgo biloba extract combined with donepezil hydrochloride in the treatment of Chinese patients with vascular dementia: A systematic review meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 3;15:1374482. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1374482. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39021830 Free PMC article.
-
Gunao-Yizhi decoction combined with donepezil for vascular dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Oct 7;101(40):e30971. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030971. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36221397 Free PMC article.
-
Butylphthalide combined with donepezil for the treatment of vascular dementia: a meta-analysis.J Int Med Res. 2024 Mar;52(3):3000605231223081. doi: 10.1177/03000605231223081. J Int Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38546241 Free PMC article.
-
Donepezil in vascular dementia: combined analysis of two large-scale clinical trials.Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2005;20(6):338-44. doi: 10.1159/000088494. Epub 2005 Sep 23. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2005. PMID: 16192723 Clinical Trial.
-
Therapeutic effect of piracetam with nimodipine on vascular dementia after cerebral infarction.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2020 Sep;33(5(Special)):2405-2411. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 33832882
Cited by
-
Comparison of the effects of citicoline and vascular rehabilitation capsules on neurotrophic and inflammatory factors in patients with cerebral infarction.J Med Biochem. 2025 Jul 4;44(4):724-730. doi: 10.5937/jomb0-55775. J Med Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40837354 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidative Effect of Amomum testaceum Ridl. Extract for Protecting against Vascular Dementia.Int J Food Sci. 2022 Dec 29;2022:1572527. doi: 10.1155/2022/1572527. eCollection 2022. Int J Food Sci. 2022. PMID: 36618764 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Combined Application of Donepezil and Nimodipine on Patients with Comorbid Cerebral Small Vessel Disease and Cognitive Dysfunction: Efficacy and Influence on Nutritional Status.Actas Esp Psiquiatr. 2024 Aug;52(4):533-541. doi: 10.62641/aep.v52i4.1647. Actas Esp Psiquiatr. 2024. PMID: 39129693 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome-Mediated Delivery of Amyloid Beta Modulators: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jul 8. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-05189-6. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40627107 Review.
References
-
- Wolters FJ, Ikram MA. Epidemiology of vascular dementia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2019;39:1542–9. - PubMed
-
- Zhuo M, Yue CH, Wan-yu F. System review of efficacy of donepezil in treatment of vascular dementia. Chin J New Drugs 2013;22:569–76.
-
- Tao CH, Ling L, Deng CH, et al. . Efficacy and safety of nimodipine in treatment of vascular dementia: a systematic review. Chin J Contemp Neurol Neurosurg 2015;15:546–53.
-
- Bing L, Dongmei L, Yin Zh. Efficacy of the combination of donepezil and nimodipine in the treatment of vascular dementia. Chin J Gerontol 2020;40:3279–81.
-
- Tao-zuo Zh. Clinical observation of 72 cases of vascular dementia patients treated with donepezil combined with nimodipine. Chin J Integr Med Cardio-/Cerebrovasc Dis 2020;18:1663–4.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

