Comparison of a multitarget blood test to ultrasound and alpha-fetoprotein for hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance: Results of a network meta-analysis
- PMID: 35945907
- PMCID: PMC9512471
- DOI: 10.1002/hep4.2045
Comparison of a multitarget blood test to ultrasound and alpha-fetoprotein for hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance: Results of a network meta-analysis
Abstract
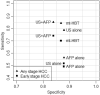
Ultrasound-based surveillance has suboptimal sensitivity for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in patients with cirrhosis. There are several emerging alternatives, including a novel multitarget HCC blood test (Mt-HBT). We compared performance of mt-HBT against ultrasound with or without alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) for early HCC detection in patients with cirrhosis. Per the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines, two reviewers searched PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, and clinicaltrials.gov databases from January 1990 through December 2020 to identify studies reporting sensitivity and/or specificity of ultrasound and AFP for overall and early stage HCC detection in patients with cirrhosis. Mt-HBT diagnostic performance was derived from a clinical validation study. A network meta-analysis model was built for comparative assessment, and pooled estimates of sensitivity at a fixed specificity were estimated based on Bayesian binormal receiver operating characteristic models for each modality. Forty-one studies (comprising 62,517 patients with cirrhosis) met inclusion criteria. Ultrasound-alone sensitivity was 51.6% (95% credible interval [CrI], 43.3%-60.5%) for early stage HCC detection, which increased with the addition of AFP to 74.1% (95% CrI, 62.6%-82.4%); however, this was offset by decreased specificity (87.9% vs. 83.9%, respectively). With specificity fixed at 90%, mt-HBT sensitivity for early stage HCC detection was higher than ultrasound alone (18.2%; 95% CrI, 0.2%-37.7%) and similar to ultrasound with AFP (-3.3%; 95% CrI, -22.3%-17.4%). Pairwise posterior probabilities suggested a preference for mt-HBT over ultrasound alone in 97.4% of cases but only 36.3% of cases versus ultrasound with AFP. Conclusion: A blood-based mt-HBT has higher sensitivity than ultrasound alone for early stage HCC detection but similar sensitivity compared to ultrasound and AFP. Mt-HBT could be a comparable alternative to existing methods for HCC surveillance in patients who are at risk.
© 2022 The Authors. Hepatology Communications published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Amit Singal has served as a consultant or on advisory boards for Exact Sciences, FujiFilm Medical Sciences, Glycotest, Roche, Bayer, and GRAIL. Neehar Parikh has served as a consultant or on advisory boards for Exact Sciences, Eli Lilly, Eisai, Genentech, Freenome, Fujifilm Medical Sciences, and Exelixis; he received grants from Glycotest. Burak Ozbay is a full‐time employee and shareholder of Exact Sciences. Jagpreet Chhatwal served as a consultant to Bayer, NovoNordisk, and Flatiron Health and is a partner and shareholder of Value Analytics Labs. Turgay Ayer is a partner and shareholder of Value Analytics Labs. Benjamin Haaland consults for the National Kidney Foundation, Value Analytics Health, Avidity Partners Management, and Ally Bridge. Kyle Porter is a shareholder of Exact Sciences. Carol Kirshner has nothing to report.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

