Detection of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images: Boosting the performance with convolutional neural network and transfer learning
- PMID: 35945966
- PMCID: PMC9353436
- DOI: 10.1111/exsy.13099
Detection of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images: Boosting the performance with convolutional neural network and transfer learning
Abstract
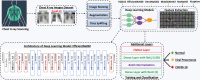
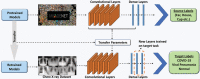
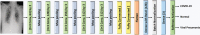
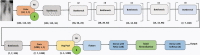
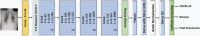
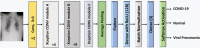
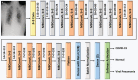
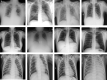
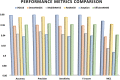
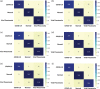
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is a pandemic that has caused thousands of casualties and impacts all over the world. Most countries are facing a shortage of COVID-19 test kits in hospitals due to the daily increase in the number of cases. Early detection of COVID-19 can protect people from severe infection. Unfortunately, COVID-19 can be misdiagnosed as pneumonia or other illness and can lead to patient death. Therefore, in order to avoid the spread of COVID-19 among the population, it is necessary to implement an automated early diagnostic system as a rapid alternative diagnostic system. Several researchers have done very well in detecting COVID-19; however, most of them have lower accuracy and overfitting issues that make early screening of COVID-19 difficult. Transfer learning is the most successful technique to solve this problem with higher accuracy. In this paper, we studied the feasibility of applying transfer learning and added our own classifier to automatically classify COVID-19 because transfer learning is very suitable for medical imaging due to the limited availability of data. In this work, we proposed a CNN model based on deep transfer learning technique using six different pre-trained architectures, including VGG16, DenseNet201, MobileNetV2, ResNet50, Xception, and EfficientNetB0. A total of 3886 chest X-rays (1200 cases of COVID-19, 1341 healthy and 1345 cases of viral pneumonia) were used to study the effectiveness of the proposed CNN model. A comparative analysis of the proposed CNN models using three classes of chest X-ray datasets was carried out in order to find the most suitable model. Experimental results show that the proposed CNN model based on VGG16 was able to accurately diagnose COVID-19 patients with 97.84% accuracy, 97.90% precision, 97.89% sensitivity, and 97.89% of F1-score. Evaluation of the test data shows that the proposed model produces the highest accuracy among CNNs and seems to be the most suitable choice for COVID-19 classification. We believe that in this pandemic situation, this model will support healthcare professionals in improving patient screening.
Keywords: COVID‐19 detection; VGG16; chest X‐rays; deep CNN; medical image analysis; transfer learning.
© 2022 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Al‐Zu'bi, S. , Al‐Ayyoub, M. , Jararweh, Y. , & Shehab, M. A. (2017). Enhanced 3D segmentation techniques for reconstructed 3D medical volumes: Robust and accurate intelligent system. Procedia Computer Science, 113, 531–538.
-
- AlZu'bi, S. , Al‐Qatawneh, S. , & Alsmirat, M. (2018). Transferable HMM trained matrices for accelerating statistical segmentation time. Paper presented at the 2018 fifth international conference on social networks analysis, management and security (SNAMS).
-
- AlZu'bi, S. , Aqel, D. , & Mughaid, A. (2021). Recent intelligent approaches for managing and optimizing smart blood donation process. Paper presented at the 2021 international conference on information technology (ICIT).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
