HLA-G 3'UTR polymorphisms & response to a yoga-based lifestyle intervention in rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 35946202
- PMCID: PMC9629524
- DOI: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_3196_20
HLA-G 3'UTR polymorphisms & response to a yoga-based lifestyle intervention in rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background & objectives: Human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-G plays a vital role in immunomodulation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The mounting evidence suggests a link between HLA-G gene polymorphisms, disease susceptibility and methotrexate treatment response. Various environmental factors influence the onset and progression of RA and its treatment outcomes. The aim is to identify the treatment response of HLA-G 3' untranslated region polymorphisms to yoga-based lifestyle intervention (YBLI).
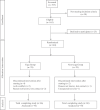
Methods: In this eight-week single-blinded randomized controlled trial (CTRI/2017/05/008589), patients with RA (n=140) were randomized into two groups namely, yoga group or non-yoga group. Baseline genomic DNA was isolated using salting-out method. PCR-based methods were used for genotyping. The levels of soluble (s) HLA-G and disease activity were assessed by ELISA and disease activity score-28-erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR), respectively, at baseline (day 0) and after eight weeks of intervention.
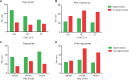
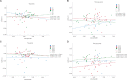
Results: Low-producing sHLA-G genotypes, i.e. +3142GG and 14 bp ins/ins, showed a significant increase in sHLA-G levels after YBLI. The association analysis between HLA-G polymorphisms and treatment for RA showed no considerable differential treatment remission in either of the groups (P>0.05). The percentages of improvement were higher in the yoga group as compared to the non-yoga group in both the HLA-G +3142G>C and 14 bp ins/del polymorphisms irrespective of their respective genotypes. No significant association was found between sHLA-G levels and disease activity with respect to genotypes.
Interpretation & conclusions: Yoga intervention results in improvement and reduced severity of RA in patients irrespective of the HLA-G 14 bp ins/del or +3142G>C polymorphisms. YBLI may be used as an adjunct therapy in RA independent of the genotypes.
Keywords: 3'UTR HLA-G; DAS28-ESR; gene environment interaction; polymorphism; randomized controlled trial; rheumatoid arthritis; soluble HLA-G.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Yoga, rheumatoid arthritis & human leukocyte antigen-G.Indian J Med Res. 2022 Feb;155(2):225-226. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.ijmr_785_22. Indian J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35946198 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
