Development of a cost-effective ex vivo lung perfusion system for lung transplantation in India
- PMID: 35946207
- PMCID: PMC9629529
- DOI: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_27_19
Development of a cost-effective ex vivo lung perfusion system for lung transplantation in India
Abstract
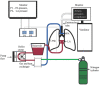
Background & objectives: Standard donor lung preservation with cold flush and storage allows up to six hours between retrieval of lungs from the donor and transplantation in the recipient. Ex vivo lung perfusion (EVLP) systems mimic physiological ventilation and perfusion in the donor lungs with potential for prolonged lung preservation and donor lung reconditioning. In this study, it was aimed to perform EVLP on discarded donor lungs using a locally developed EVLP system.
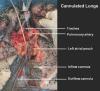
Methods: Equipment that are routinely used for cardiac surgeries were collected and a functional EVLP system was assembled. This system was used on five pairs of lungs retrieved from brain-dead organ donors. The lungs were ventilated and pulmonary circulation was continuously perfused with a solution containing oxygen and nutrients for four hours. The system was tested without red blood cells (RBCs) added to the solution (acellular group; n=3; A1, A2 and A3) and also with RBCs added to the solution (cellular group; n=2; C1 and C2).
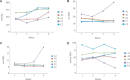
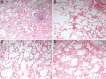
Results: The EVLP system was successfully used in four (A1, A2, A3 and C2) of the five lung pairs. Mechanical and gas exchange functions of the lungs were preserved in these lung pairs. One lung pair (C1) worsened and developed pulmonary oedema. Histopathological examination of all five lung pairs was satisfactory at the end of the procedure. Major challenges faced were leakage of solution from the system and obstruction to drainage of RBCs containing solution from the lungs.
Interpretation & conclusions: The results of the present study suggest that, it is possible to maintain the lungs retrieved for transplantation in a physiological condition using a locally prepared EVLP system and a solution without RBCs.
Keywords: Erythrocytes; lung transplantation; organ preservation; organ preservation solutions; perfusate.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prolonged EVLP Using OCS Lung: Cellular and Acellular Perfusates.Transplantation. 2017 Oct;101(10):2303-2311. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001616. Transplantation. 2017. PMID: 28009782 Free PMC article.
-
Ex vivo rehabilitation of non-heart-beating donor lungs in preclinical porcine model: delayed perfusion results in superior lung function.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012 Nov;144(5):1208-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2012.07.056. Epub 2012 Aug 31. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012. PMID: 22944084 Free PMC article.
-
Technique for prolonged normothermic ex vivo lung perfusion.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2008 Dec;27(12):1319-25. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2008.09.003. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2008. PMID: 19059112
-
Current status and future potential of ex vivo lung perfusion in clinical lung transplantation.Artif Organs. 2023 Nov;47(11):1700-1709. doi: 10.1111/aor.14607. Epub 2023 Jul 16. Artif Organs. 2023. PMID: 37455548 Review.
-
The Conversional Efficacy of Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion and Clinical Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Transplantation of Donor Lungs by Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion: A Meta-Analysis.Ann Transplant. 2019 Dec 27;24:647-660. doi: 10.12659/AOT.919242. Ann Transplant. 2019. PMID: 31879416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van Raemdonck D. Thoracic organs:Current preservation technology and future prospects;part 1:Lung. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2010;15:150–5. - PubMed
-
- Thabut G, Mal H, Cerrina J, Dartevelle P, Dromer C, Velly JF, et al. Graft ischemic time and outcome of lung transplantation:A multicenter analysis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;171:786–91. - PubMed
-
- Van Raemdonck D, Neyrinck A, Verleden GM, Dupont L, Coosemans W, Decaluwé H, et al. Lung donor selection and management. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2009;6:28–38. - PubMed
-
- Steen S, Sjöberg T, Pierre L, Liao Q, Eriksson L, Algotsson L. Transplantation of lungs from a non-heart-beating donor. Lancet. 2001;357:825–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
