Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on Notch signaling pathway after severe carbon monoxide poisoning in mice
- PMID: 35946219
- PMCID: PMC9480357
- DOI: 10.4103/2045-9912.344971
Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on Notch signaling pathway after severe carbon monoxide poisoning in mice
Abstract
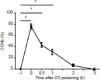
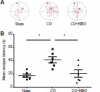
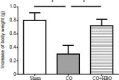
Demyelination of the cerebral white matter is the most common pathological change after carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning. Notch signaling, the mechanism underlying the differentiation of astrocytes and oligodendrocytes, is critical to remyelination of the white matter after brain lesion. The purpose of this work was to determine the effects of hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) on Notch signaling pathway after CO poisoning for the explanation of the protective effects of HBO on CO-poisoning-related cerebral white matter demyelination. The male C57 BL/6 mice with severe CO poisoning were treated by HBO. And HBO therapy shortened the escape latency and improved the body mass after CO poisoning. HBO therapy also significantly suppressed protein and mRNA levels of Notch1 and Hes5 after CO poisoning. Our findings suggested that HBO could suppress the activation of Notch signaling pathway after CO poisoning, which is the mechanism underlying the neuroprotection of HBO on demyelination after severe CO poisoning.
Keywords: Hes5; Notch signaling pathway; carbon monoxide poisoning; carboxyhemoglobin; demyelination; hyperbaric oxygen; oligodendrocyte; oligodendrocyte precursor cell; remyelination; white matter.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures


References
-
- Hampson NB, Little CE. Hyperbaric treatment of patients with carbon monoxide poisoning in the United States. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2005;32:21–26. - PubMed
-
- Hampson NB, Weaver LK. Carbon monoxide poisoning: a new incidence for an old disease. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2007;34:163–168. - PubMed
-
- Weaver LK. Clinical practice. Carbon monoxide poisoning. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1217–1225. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

