Mineral and bone disorder and longterm survival in a chronic kidney disease grade 3b-4cohort
- PMID: 35946486
- PMCID: PMC9373789
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2107543
Mineral and bone disorder and longterm survival in a chronic kidney disease grade 3b-4cohort
Abstract
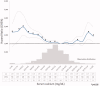
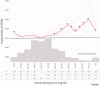
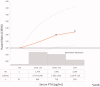
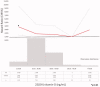
Mineral and bone disorder biomarkers 'normal ranges' are controversial. The aim of the study was to evaluate the association between serum calcium (Ca), phosphate (P), intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH), and 25(OH) vitamin D levels and mortality risk, in a chronic kidney disease (CKD) grade (G) 3b-4 cohort. The Uruguayan National Renal Healthcare Program (NRHP-UY) CKD patients' cohort, included between 1 October 2004 and 1 March 2020 and followed-up until 1 March 2021, was analyzed with the Ethics Committee approval. A total of 6473 patients were analyzed: 56% men, median age 73 (65-79) years, 55% on CKD G3b. At the end of the follow-up, 2459 (37.7%) patients had died (6.4/100 patient-year). There were iPTH data on 2013 patients (younger, with lower estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and lesser comorbidities). By bivariate Cox analysis the lowest death risk was observed with mean Ca between 9.01 and 10.25 mg/dl, P between 2.76 and 4.0 mg/dl, iPTH ≤ 105 pg/ml, and 25(OH) vitamin D >10 ng/ml. The multivariate Cox regression mortality risk adjusted to age, sex, CKD etiology, diabetes, smoking, cardiovascular comorbidity, blood pressure, proteinuria, eGFR, renin-angiotensin system blockers and vitamin D treatments, serum Ca, P, iPTH, and 25(OH) vitamin D (n = 964) showed that a higher mortality risk was associated with p > 4.00 mg/dl (HR 1.668, CI 95%: 1.201-2.317), iPTH >105 pg/ml (HR 1.386, CI 95%: 1.012-1.989), and 25(OH) vitamin D ≤ 10 ng/ml (HR 1.958, CI 95%: 1.238-3.098) and a lower mortality risk with 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D treatment (HR 0.639, CI 95%: 0.451-0.906). These data may contribute to the precise G3b-4 CKD-MBD biomarkers levels definition.
Keywords: Calcium; chronic kidney disease 3b-4; mineral metabolism; parathyroid hormone; phosphate; survival analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Moe S, Drüeke T, Cunningham J, et al. Definition, evaluation, and classification of renal osteodystrophy: a position statement from kidney disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2006;69(11):1945–1953. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, et al. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(13):1296–1305. (Erratum in: N Engl J Med. 2008;18(4):4). - PubMed
-
- Felsenfeld AJ, Levine BS, Rodriguez M.. Pathophysiology of calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium dysregulation in chronic kidney disease. Semin Dial. 2015;28(6):564–577. - PubMed
-
- Evenepoel P, Rodriguez M, Ketteler M.. Laboratory abnormalities in CKD-MBD: markers, predictors, or mediators of disease? Semin Nephrol. 2014;34(2):151–163. - PubMed
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD-MBD Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD). Kidney Int Suppl. 2009;113:S1–S130. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
