Renin and electrolytes indicate the mineralocorticoid activity of fludrocortisone: a 6 year study in primary adrenal insufficiency
- PMID: 35947299
- PMCID: PMC9829625
- DOI: 10.1007/s40618-022-01889-1
Renin and electrolytes indicate the mineralocorticoid activity of fludrocortisone: a 6 year study in primary adrenal insufficiency
Abstract
Context: Fludrocortisone (FC) is the mineralocorticoid (MC) replacement treatment for patients with primary adrenal insufficiency (PAI).
Objective: To explore the dose of FC treatment and its relationship with glucocorticoid therapy, sodium, potassium, renin and clinical parameters.
Setting: Monocentric cohort.
Patients: Data of 193 patients with PAI (130 autoimmune) were collected during baseline (T0), intermediate (T1) and last follow-up visit (T2, respectively, after a mean of 38 and 72 months).
Main outcome measure: Utility of endocrine and clinical parameters to titrate FC dose.
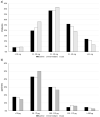
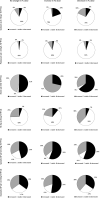
Results: FC dose (50-75 μg/daily) was stable in the follow-up in half patients. The MC activity of FC was dose-dependent: we observed a reduced but significant positive linear correlation between FC dose and sodium (r = 0.132) and negative linear correlation between FC and potassium (r = - 0.162) or renin (r = - 0.131, all p < 0.01). An overall reduction in the FC dose was observed at T2 in the group with longer follow-up (> 60 months, p < 0.05). Higher doses of FC were observed in patients with low-normal renin, especially in autoimmune PAI (86 vs 65 μg/daily, p < 0.05). On the contrary, reduced sodium and increased potassium levels were observed in patients with high renin at T2. The number of cardiovascular events (15 in the whole cohort) was similar in patients sorted by renin levels or FC dose.
Conclusions: Renin and electrolytes can indicate the MC activity of FC treatment: they should be routinely evaluated and used to titrate its dose that can be reduced in the long-term follow-up.
Keywords: Fludrocortisone; Mineralocorticoid treatment; Primary adrenal insufficiency; Renin.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest that might be perceived as influencing the impartiality of the reported research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of plasma renin activity in evaluating the adequacy of mineralocorticoid replacement in primary adrenal insufficiency.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1996 Nov;45(5):529-34. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2265.1996.00838.x. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1996. PMID: 8977748
-
Use of plasma renin activity to monitor mineralocorticoid treatment in dogs with primary hypoadrenocorticism: desoxycorticosterone versus fludrocortisone.J Vet Intern Med. 2014 Sep-Oct;28(5):1471-8. doi: 10.1111/jvim.12426. J Vet Intern Med. 2014. PMID: 25274440 Free PMC article.
-
Atrial natriuretic peptide and plasma renin levels in assessment of mineralocorticoid replacement in Addison's disease.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996 Apr;81(4):1411-5. doi: 10.1210/jcem.81.4.8636343. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996. PMID: 8636343 Clinical Trial.
-
Mineralocorticoid substitution and monitoring in primary adrenal insufficiency.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Jan;29(1):17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2014.08.008. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 25617169 Review.
-
Management of adrenal insufficiency in different clinical settings.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005 Nov;6(14):2407-17. doi: 10.1517/14656566.6.14.2407. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005. PMID: 16259572 Review.
Cited by
-
Performance of renin assays in selecting fludrocortisone dose in children with adrenal disorders.Endocr Connect. 2024 Jan 22;13(2):e230370. doi: 10.1530/EC-23-0370. Print 2024 Feb 1. Endocr Connect. 2024. PMID: 38165389 Free PMC article.
-
Mineralocorticoid effects of fludrocortisone and hydrocortisone in primary adrenal insufficiency: EU-AIR patient data.J Endocrinol Invest. 2025 Sep 6. doi: 10.1007/s40618-025-02657-7. Online ahead of print. J Endocrinol Invest. 2025. PMID: 40913682
-
Addison's Disease: Diagnosis and Management Strategies.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Jun 2;16:2187-2210. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S390793. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 37287503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma Renin: A Useful Marker for Mineralocorticoid Adjustment in Patients With Primary Adrenal Insufficiency.J Endocr Soc. 2024 Oct 11;8(11):bvae174. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvae174. eCollection 2024 Sep 26. J Endocr Soc. 2024. PMID: 39416427 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing treatment adherence is crucial to determine adequacy of mineralocorticoid therapy.Endocr Connect. 2023 Aug 2;12(9):e230059. doi: 10.1530/EC-23-0059. Endocr Connect. 2023. PMID: 37410094 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

